![Forming and Formability of AHSS]()
Forming
Introduction
Approaches for forming higher strength steels evolved with the commercialization of increased strength levels of High Strength Low Alloy (HSLA) steels. Demands for greater crash performance while simultaneously reducing mass and cost have spawned the development of new groups of steels that improve on the properties of these HSLA steels. Forming of Advanced High-Strength Steel (AHSS) is not a radical change from forming conventional HSLA steels, providing some of the key differences are understood and accounted for in die design, die process, and equipment selection.
AHSS grades solve two distinct automotive needs by two different groups of steels. The first group as a class has higher strength levels with improved formability and crash-energy absorption compared to HSLA grades. DP, TRIP, FB, and TWIP steels, which have increased values of the work hardening exponent (n-value), fulfill this requirement. The second group, including CP and MS steels, extends the availability of steel in strength ranges above what is available with HSLA grades. Originally targeted for chassis, suspension, and body-in-white components, AHSS grades are now being applied to doors and other body panels. New variations in microstructure help meet specific process requirements, including increased edge stretch, bendability, strengthening after forming, or tighter property tolerances.
The progressive increases in yield and tensile strength with these new AHSS grades magnifies existing forming issues with conventional HSLA grades and creates new challenges. Concerns include higher loads on processing equipment including presses, levelers, straighteners, blanking lines, coil slitting lines and roll forming equipment. Additionally, there are material and surface treatment considerations required for tooling in the stamping plants: draw dies, trim steels, and flange steels. Compared to conventional HSLA steels, greater energy requirements result from higher AHSS yield strengths, tensile strengths and significantly higher work hardening rates. This places new requirements on press capacity, leveler, straightener and slitting capabilities, tool construction/protection, lubricant capabilities, part and process design, and maintenance. Springback management becomes more critical as yield strengths continue to increase. Conventional and press hardened (hot formed) AHSS parts have very high strength after forming, so re- forming operations should be avoided. Trimming, cutting, and piercing equipment must be constructed and maintained to overcome the extreme high strength of the final stamping. Laser cutting of press hardened parts produces a finished part that avoids pushing the limits of trim and pierce tools and dies utilized for conventional HSLA steel.
There are an ever-increasing number of AHSS multiphase microstructure grades available, each designed to resist various forming failure modes while achieving final part performance requirements. Sharing of information regarding the planned part geometry, die and stamping processing, and final part application between steel suppliers, product and die process engineering, and end users helps ensure selection of the right steel grade for the application. This becomes especially relevant since multiphase microstructures experience additional forming failure modes compared with conventional high strength products.
Tool Design Considerations
The characteristics associated with different AHSS grades influence die design and die processing decisions. Not only are these steels typically higher in strength, but they also undergo substantial work hardening during forming. These lead to increased local loads, and changes in friction, die wear, and press requirements. The multiphase microstructures increase cut edge and bending fracture sensitivity. As such, extending the life and performance of tooling in press shops requires a rethinking of tool and part design.
Part Design
Successful application of any material requires close coordination of part design and the manufacturing process. Consult product and manufacturing process engineers when designing AHSS parts to understand both the limitations and advantages of the grade and the proper forming process to be employed. Start in the concept and feasibility stage to ensure sufficient time for corrective actions and optimization.
Soft tool materials like kirksite may be used for manufacturing prototype parts and the inserts used to eliminate local wrinkles or buckles. However, wear resistant coatings are typically not applied to these tool surfaces, so the metal flow seen in these prototype parts may not match the metal flow seen under production conditions. The results from soft tool tryouts should not be used to assess manufacturability and springback of AHSS parts.
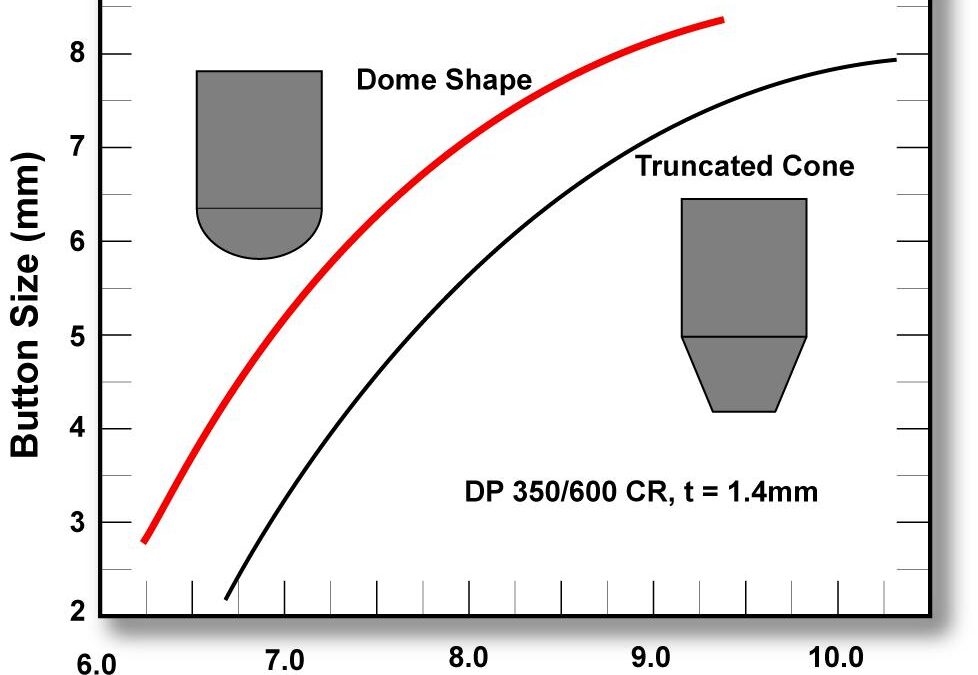
Design structural frames (such as rails, sills, cross members, and roof bows) as open-ended channels to permit forming operations rather than draw die processes. AHSS stampings requiring closed-end draw operations are limited by a reduced depth of draw, Figure 1. Less complex, open-ended stamped channels are less limited in depth. A rule of thumb is that DP 350Y600T can be formed to only half the draw depth of a mild steel.

Figure 1: Schematic of an open end part design (left) and a closed end part design (right). The open-ended design allows for greater depths when utilizing AHSS versus the closed ended design historically used with mild steel.A-5
Where possible, avoid closed-end developments to make more complex geometries with AHSS grades. Wrapping ends of “hat” sections increases forming loads, increases the chances of circumferential compression wrinkling on the binder, specifically in the corners, and increases wrinkling on the draw wall if the blank edge runs through the draw bead. Draw die developments that include a closed (or wrapped) end development usually also require a larger blank size. During draw die development, it is best to identify parts that have a “hat” section geometry in certain locations and develop the draw die accordingly to maximize the positive formability attributes of AHSS while minimizing the limitations of AHSS.
For example, the left image in Figure 2 shows a draw die development on a DP600 cowl side with a closed (wrapped) end, with the right image showing a similar part developed with an open end. Although both final part geometries are similar, the closed-end development led to significant global formability failures due to the excessive stretch. In contrast, the open-ended development had virtually no global formability related failures. Other design and die development differences in the part on the right include the use of stake beads to control springback and embossments to eliminate wavy metal. In addition, an open-ended development has the potential to reduce the blank size for material utilization savings.

Figure 2: Draw die development for a cowl side formed from DP600. Left image: closed-end development with global formability failures, waviness, and springback. Right image: open-ended development with no splits, waves, or dimensional concerns.U-6
The automotive industry has adopted a strategy for “lighter dies and fewer dies”, to reduce cost. One key element is “part consolidation”, such as one-piece body side outers and inners. High strength steels challenge the part consolidation mantra. When encountering extreme formability challenges, parts previously made with one set of dies when stamped from lower strength steels may benefit from transitioning to a laser welded blank with a lower strength grade in the challenging region and higher strength steels in the remainder of the part. Alternatively, splitting the consolidated part into two or more separate parts subsequently welded together may improve stamping success at the expense of another operation. In the past, one-piece rocker panels were stamped from conventional mild or HSLA steel. However, this component requires higher strength and reduced thickness to meet weight and crash requirements, so now DP980 is often considered as the grade of choice for this application. Figure 3 shows a rocker panel where insufficient formability of DP980 prevented a one-piece stamping. The OEM solved this by dividing the part into two stampings, putting a more formable grade where needed on the wrapped (or closed) end.

Figure 3: When a one-piece rocker panel could not be successfully formed from DP980, the OEM stamped a DP980 rocker panel section with an open-ended design and spot welded it to a mild steel end cap.U-6
Trim and Pierce Tool Design
- Trim and pierce tools need to withstand higher loads since AHSS grades have higher tensile strengths than conventional high-strength steels.
- Edge cracking is minimized with proper support of the trim stock during trimming.
- Modify timing of the trim/pierce operation to minimize snap-through reverse loading.
- Scrap shedding may be an issue, since AHSS springback can cause scrap to stick in the tool.
Flange Design
- Design more formable flanges to reduce need for extra re-strike operations.
- Areas to be flanged should have a “break-line” or initial bend radius drawn in the first die to reduce springback.
- Adapt die radii for material strength and blank thickness.
Draw Bead Design
- Metal flow across draw beads generates strain and minimizes the elastic recovery which causes springback.
- Metal flow across draw beads generates large amounts of work hardening, leading to increased press loads.
- Optimizing blank size and shape reduces the reliance on draw beads, which can excessively work harden the material before entering the die opening.
Guidelines to Avoid Edge Cracking During Stretch Flanging
- Flange length transition should be gradual – abrupt changes in flange length cause local stress raisers leading to edge cracks.
- Use good cutting practices to achieve a high-quality edge.
- Avoid the use of sharp notch features in curved flanges.
- Avoid putting bypass notches in stretch or compression edges of blanks or progressive die carrier strips. These bypass notches can act as stress risers and lead to edge fractures in the draw or flange operation. In addition, bypass notches in blanks and progressive dies are difficult to maintain, which can increase the potential for edge fracture.
- Metal gainers in the draw die or in the die prior to the stretch flange operation compensates for change in length of line that occurs during flanging, helping to avoid edge cracking. In the example shown in Figure 4, edge fractures moved from the draw panel to flanged panel after grinding on the draw die to eliminate edge fractures in the draw operation. The draw panel underneath the flanged part in Figure 4 did not have edge fractures. The reduction in the length of line in the draw operation moved the problem to the flanged part where the stamping transitioned from bending and straightening in the flange operation to a stretch flange operation. A better practice is to add metal gainers to the draw panel to provide the feedstock which expands during stretch flanging.

Figure 4: Flanged panel fractures, with the draw panel underneath. Adding metal gainers to the draw panel would help minimize these fractures.U-6
- The higher strength of AHSS makes it more difficult to pull out loose metal or achieve a minimum stretch in flat sections of stampings. Addendum, metal gainers (Figures 5 and 6), and other tool features balance lengths of line and locally increase stretch.

Figure 5: Metal gainers help avoid insufficient stretched areas and eliminate buckles.T-3

Figure 6: Metal gainers and depressions balance stresses and minimizes wrinkled metal.A-41
![Forming and Formability of AHSS]()
Mechanical Properties
Introduction to Mechanical Properties
Tensile property characterization of mild and High Strength Low Alloy steel (HSLA) traditionally was tested only in the rolling direction and included only yield strength, tensile strength, and total elongation. Properties vary as a function of orientation relative to the rolling (grain) direction, so testing in the longitudinal (0°), transverse (90°), and diagonal (45°) orientations relative to the rolling direction is done to obtain a better understanding of metal properties (Figure 1).
A more complete perspective of forming characteristics is obtained by also considering work hardening exponents (n-values) and anisotropy ratios (r-values), both of which are important to achieve improved and consistent formability.

Figure 1. Tensile Test Sample Orientation Relative to Rolling Direction
Hardness readings are sometimes included in this characterization, but hardness readings are of little use in assessing formability requirements for sheet steel. Hardness testing is best used to assess the heat treatment quality and durability of the tools used to roll, stamp, and cut sheet metal.
The formability limits of different grades of conventional mild and HSLA steels were learned by correlating press performance with as-received mechanical properties. This information can be fed into computer forming simulation packages to run tryouts and troubleshooting in a virtual environment. Many important parameters can be measured in a tensile test, where the output is a stress-strain curve (Figure 2).

Figure 2: Representative Stress-Strain Curve Showing Some Mechanical Properties
Press shop behavior of Advanced High-Strength Steels is more complex. AHSS properties are modified by changing chemistry, annealing temperature, amount of deformation, time, and even deformation path. With new microstructures, these steels become “Designer Steels” with properties tailored not only for initial forming of the stamping but in-service performance requirements for crash resistance, energy absorption, fatigue life, and other needs. An extended list of properties beyond a conventional tensile test is now needed to evaluate total performance with virtual forming prior to cutting the first die, to ensure ordering and receipt of the correct steel, and to enable successful troubleshooting if problems occur.
With increasing use of advanced steels for value-added applications, combined with the natural flow of more manufacturing occurring down the supply chain, it is critical that all levels of suppliers and users understand both how to measure the parameters and how they affect the forming process.
Highlights
-
- The multiphase microstructure in Advanced High Strength Steels results in properties that change as the steel is deformed. An in-depth understanding of formability properties is necessary for proper application of these steels.
- Tensile test data characterizes the ability of a steel grade to perform with respect to global (tensile and necking) formability. Different tests like hole expansion and bending characterize performance at cut edges or bend radii.
- DP steels have higher n-values in the initial stages of deformation compared to conventional HSLA grades. These higher n-values help distribute deformation more uniformly in the presence of a stress gradient and thereby help minimize strain localization that would otherwise reduce the local thickness of the formed part.
- The n-value of certain AHSS grades, including dual phase steels, is not constant: there is a higher n-value at lower strains followed by a drop as strain increases.
- TRIP steels have a smaller initial increase in n-value than DP steels during forming but sustain the increase throughout the entire deformation process. Part designers can use these steels to achieve more complex geometries or further reduce part thickness for weight savings.
- TRIP steels have retained austenite after forming that transforms into martensite during a crash event, enabling improved crash performance.
- Normal anisotropy values (rm) approximately equal to 1 are a characteristic of all hot-rolled steels and most cold-rolled and coated AHSS and conventional HSLA steels.
- AHSS work hardens with increasing strain rate, but the effect is less than observed with mild steel. The n-value changes very little over a 105 (100,000x) increase in strain rate.
- As-received AHSS does not age-harden in storage.
- DP and TRIP steels have substantial increase in YS due to a bake hardening effect, while conventional HSLA steels have almost none.
![Forming and Formability of AHSS]()
2ndGen AHSS, AHSS, Steel Grades
TWinning Induced Plasticity (TWIP) steels have the highest strength-ductility combination of any steel used in automotive applications, with tensile strength typically exceeding 1000 MPa and elongation typically greater than 50%.
TWIP steels are alloyed with 12% to 30% manganese that causes the steel to be fully austenitic even at room temperature. Other common alloying additions include up to 3% silicon, up to 3% aluminum, and up to 1% carbon. Secondary alloying additions include chromium, copper, nitrogen, niobium, titanium, and/or vanadium.D-29 The high alloying levels and substantially greater levels of strength and ductility place these into the 2nd Generation of Advanced High Strength Steels. Furthermore, due to the density of the major alloying additions relative to iron, TWIP steels have a density which is about 5% lower than most other steels.
Calling this type of steel TWIP originates from the characteristic deformation mode known as twinning. Deformation twins produced during sheet forming leads to microstructural refinement and high values of the instantaneous hardening rate (n-value). The resultant twin boundaries act like grain boundaries and strengthen the steel. On either side of a twin boundary, atoms are located in mirror image positions as indicated in the schematic microstructure shown in Figure 1. Figure 2 highlights the microstructure of TWIP steel after annealing and after deformation.

Figure 1: Schematic of TWIP steel microstructure.

Figure 2: TWIP steel in the annealed condition (left) and after deformation (right) showing deformation twins. The number of deformation twins increases with increasing strain.K-42
EDDS or Interstitial-Free or Ultra-Low Carbon steels are different descriptions for the most formable lower-strength steel. Possible test results for this grade are 150 MPa yield strength, 300 MPa tensile strength, 22% to 25% uniform elongation, and 45% to 50% total elongation. In contrast, test results on TWIP steels may show 500 MPa yield strength, 1000 MPa tensile strength, 55% uniform elongation, and 60% total elongation.
The stress-strain curves for these two grades are compared in Figure 3. The TWIP curves show the manifestation of Dynamic Strain Aging (DSA), also known as the PLC effect, with more details to follow.

Figure 3: Uniaxial tensile stress-strain curves for an interstitial-free (IF) extra-deep-drawing steel and an austenitic Fe-18%Mn-0.6%C-1.5%Al TWIP steel. Curves are presented both terms of engineering (s,e) and true (σ,ε) stresses and strains, respectively.D-30
Figure 4 compares the results of bulge testing ferritic interstitial-free (IF) steel and austenitic Fe-18%Mn-0.6%C-1.5%Al TWIP steel. The TWIP steel is still undamaged at a dome height that is 31% larger than the IF steel dome height at failure.D-30

Figure 4: Comparison of dome testing between EDDS and TWIP.D-30
Excellent stretch formability is associated with high n-values. Shown in Figure 5 is a plot showing how the instantaneous n-value changes with applied strain. N-value increases to a value of 0.45 at an approximate true (logarithmic) strain of 0.2 and then remains relatively constant until an approximate true strain of 0.3 before increasing again. The high and uniform n-value delays necking and minimizes strain peaks. Twins continue to form at higher strains, leading to finer microstructural features and continued increases in n-value at higher strains.

Figure 5: Instantaneous n-value changes with applied strain. TWIP steels have high and uniform n-value leading to excellent stretch formability.C-30
A microstructural deformation phenomenon known as the Portevin-LeChatelier (PLC) effect occurs when deforming some TWIP steels to higher strain levels. The PLC effect is known by several other names as well, including jerky flow, discontinuous yielding, and dynamic strain aging (DSA).
The severity varies with alloy, strain rate, and deformation temperature. Figure 6 shows how DSA affects the appearance of the stress strain curve of two TWIP alloys.D-29 The primary difference in the alloy design is the curves on the right are for steel containing 1.5% aluminum, with the curves on the left for a steel without aluminum. The addition of aluminum delays the serrated flow until higher levels of strain. Note that both alloys have negative strain rate sensitivity.

Figure 6: Influence of aluminum additions on serrated flow in Fe-18%Mn-0.6%C TWIP (Al-free on the left) and Fe-18%Mn-0.6%C-1.5% Al TWIP (Al-added on the right).D-29
The primary macroscopic manifestations of the Portevin-LeChatelier (PLC) effect areD-29:
- negative strain rate sensitivity.
- stress-strain curve showing serrated or jerky flow, indicating non-uniform deformation. Strain localization takes place in propagating or static deformation bands.
- the strain rate within a localized band is typically one order of magnitude larger, while that outside the band is one order of magnitude lower, than the applied strain rate.
- limited post-uniform elongation, meaning uniform elongation is just below total elongation. Said another way, fracture occurs soon after necking initiation.
The PLC effect leads to relatively poor sheared edge expansion, as measured in a hole expansion test. Figure 7 on the left highlights the crack initiation site in a sample of highly formable EDDS-IF steel, showing the classic necking appearance with extensive thinning prior to fracture. In contrast, note the absence of necking in the TWIP steel shown in the right image in Figure 7.D-29
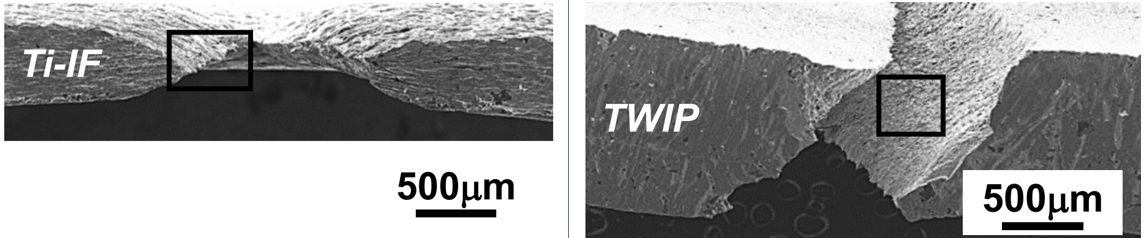
Figure 7: Sheared edge ductility comparison between IF (left) and TWIP (right) steel. TWIP steels lack the sheared edge expansion capability of IF steels.D-29
The stress-strain curves of several TWIP grades are compared in Figure 8.

Figure 8: Engineering stress-strain curve for several TWIP Grades.P-18
Complex-shaped parts requiring energy absorption capability are among the candidates for TWIP steel application, Figure 9.

Figure 9: Potential TWIP Steel Applications.N-24
Early automotive applications included the bumper beam of the 2011 Fiat Nuova Panda (Figure 10), resulting in a 28% weight savings and 22% cost savingsN-24 over the prior model which used a combination of PHS and DP steels.D-31

Figure 10: Transitioning to a TWIP Bumper Beam Resulted in Weight and Cost Savings in the 2011 Fiat Nuova Panda. N-24, D-31
In the 2014 Jeep Renegade BU/520, a welded blank combination of 1.3 mm and 1.8 mm TWIP 450/950 (Figure 11) replaced a two-piece aluminum component, aiding front end stability while reducing weight in a vehicle marketed for off-road applications.D-31

Figure 11: A TWIP welded blank improved performance and lowered weight in the 2014 Jeep Renegade BU/520.D-31
Also in 2014, the Renault EOLAB concept car where the A-Pillar Lower and the Sill Side Outer were stamped from TWIP 980 steel.R-21 By 2014, GM Daewoo used TWIP grades for A-Pillar Lowers and Front Side Members, and Hyundai used TWIP steel in 16 underbody parts. Ssangyong and Renault Samsung Motors used TWIP for Rear Side Members.I-20
Other applications include shock absorber housings, floor cross-members, wheel disks and rims, wheelhouses, and door impact beams.
A consortium called TWIP4EU with members from steel producers, steel users, research centers, and simulation companies had the goal of developing a simulation framework to accurately model the complex deformation and forming behavior of TWIP steels. The targeted part prototype component was a backrest side member of a front seat, Figure 12. Results were published in 2015.H-58

Figure 12: TWIP4EU Prototype Component formed from TWIP Steel.H-58
In addition to a complex thermomechanical mill processing requirements and high alloying costs, producing TWIP grades is more complex than conventional grades. Contributing to the challenges of TWIP production is that steelmaking practices need to be adjusted to account for the types and amounts of alloying. For example, the typical ferromanganese grade used in the production of other grades has phosphorus levels detrimental to TWIP properties. In addition, high levels of manganese and aluminum may lead to forming MnO and Al2O3 oxides on the surface after annealing, which could influence zinc coating adhesion in a hot dip galvanizing line.D-29
Critical to the performance of TWIP steels is having a microstructure that is fully austenitic. This is achieved with relatively high carbon (C > 0.5%) and manganese (Mn > 15%). These levels put the alloy at risk for hydrogen embrittlement, otherwise known as hydrogen-induced delayed fracture. Additions of aluminum were found to be effective in improving the resistance to delayed fracture. However, the levels of aluminum needed substantially reduced the castability of the molten alloy during continuous casting due to the propensity for aluminum to oxidize, which results in nozzle blockage and slag entrapment.
To reduce the amount of Al and consequently improve the castability of TWIP steels without reducing their resistance to delayed fracture, rare earth (RE) elements can be used. Rare earth metals react with H2 and form metal hydrides that are much more stable than the ordinary types of hydrogen entrapments in steels.Z-19
During annealing, manganese diffuses to the surface and oxidizes. The enriched manganese at the surface produces an oxidized layer that reduces the zinc wettability on the steel surface, and limits the ability to achieve a continuous galvanized coating. Solely using a high dew point atmosphere, such as the production strategy with QP steels, is insufficient in these high-Mn TWIP alloys.
A surface treatment process of annealing in a +10°C dew point to promote internal oxidation rather than external oxidation, combined with a subsequent pickling operation to remove any surface manganese oxides, results in a fully austenitic substrate covered by a lean-Mn decarburized ferrite layer, Figure 13. This strategy has led to the commercialization of hot-dip galvanized TWIP steels.P-32

Figure 13: Cross sectional microstructure of TWIP steel after targeted processing to improve galvanizability.P-32
Blog, main-blog
A New Software Application for Thin Wall Section Analysis
Advanced High-Strength Steel (AHSS) grades offer increased performance in yield and tensile strength. However, to fully utilize this increased strength, automotive beam sections must be designed carefully to avoid buckling of the plate elements in the section. A new software application, Geometric Analysis of Sections—GAS2.0, available through the American Iron and Steel Institute, is a tool to aid in this design effort.
Plate Buckling in Automotive Sections
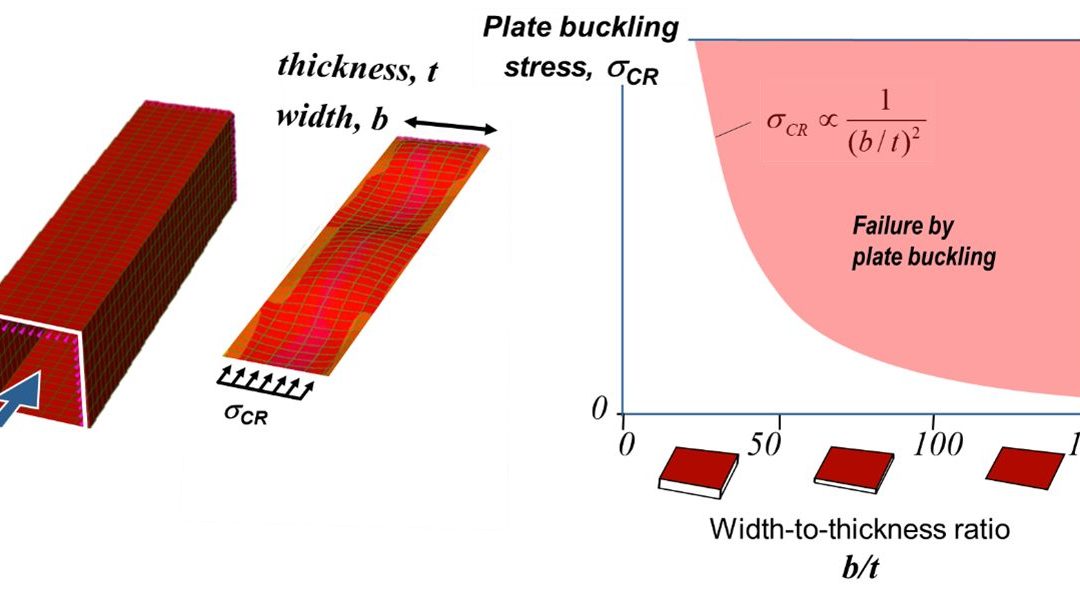
To understand how plate buckling affects the strength of a thin walled beam consider Figure 1. A square beam is made of four identical plates connected at their edges. Under an axial compressive load each plate may buckle. Considering just one of the plates, the stress that will cause buckling depends on the ratio of plate width and thickness (b/t). Thinner wider plates with large b/t ratio will buckle at a lower stress than thicker narrower plates.
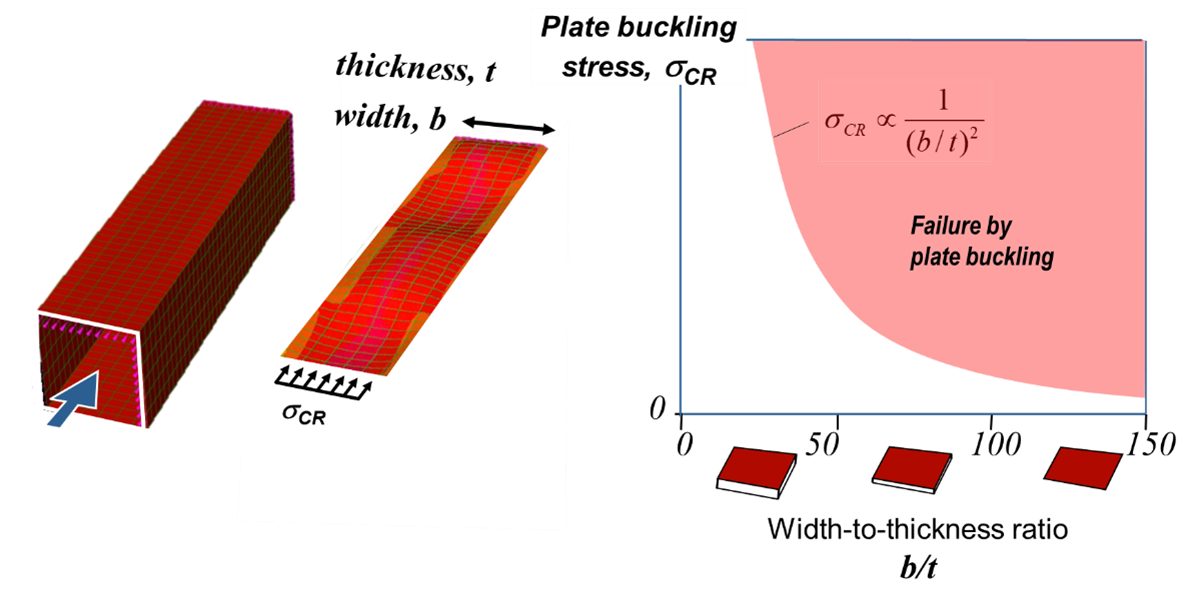
Figure 1: Plate Buckling Behavior.
Now consider a plate of mild steel (200 MPa yield stress) which has been designed to buckle just as yield stress is reached, Point A in Figure 2. The plate would have a b/t ratio of approximately 60. This design is taking full advantage of the yield strength of the material.
Now consider the same plate but substituting an AHSS grade (600 MPa yield stress) as shown in Figure 2. The plate will buckle at the same 200 MPa before reaching the material’s potential, Point B in the figure. To take advantage of this materials yield strength, the proportions of the plate will need to be changed, Point C. This illustration demonstrates the need to consider plate buckling particularly in the application of AHSS grades.
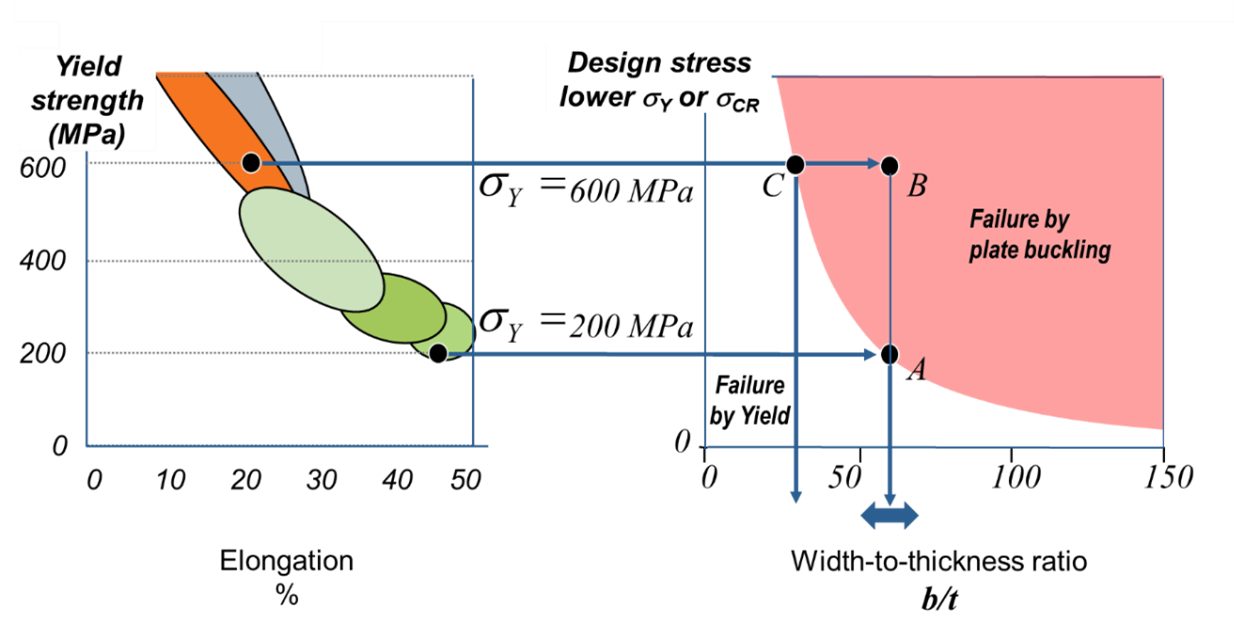
Figure 2: AHSS Substitution in a Plate.
Moving from a single plate to the more complex case of a beam section of several plates, consider Figure 3. On the left is the beam made of four plates with a compressive load causing the plates to just begin to buckle. However, this condition does not represent the maximum load carrying ability of the beam. The load can be increased until the stress at the corners of the buckled plates are at the material yield stress, center in Figure 3. Note that in this condition the stress distribution across the plate is nonlinear with lower stress in the center of each plate. One means to model this complex state is by using an imaginary Effective Section. Here the center portion is visualized as being removed and the remainder of the section is stressed uniformly at yield. The amount of plate width to be removed is determined by theory.W-21, A-42, Y-9, M-18 The effective section is a convenient way to visualize the efficiency of a section design given the material grade and provides an estimate of the maximum load carrying ability of the beam.
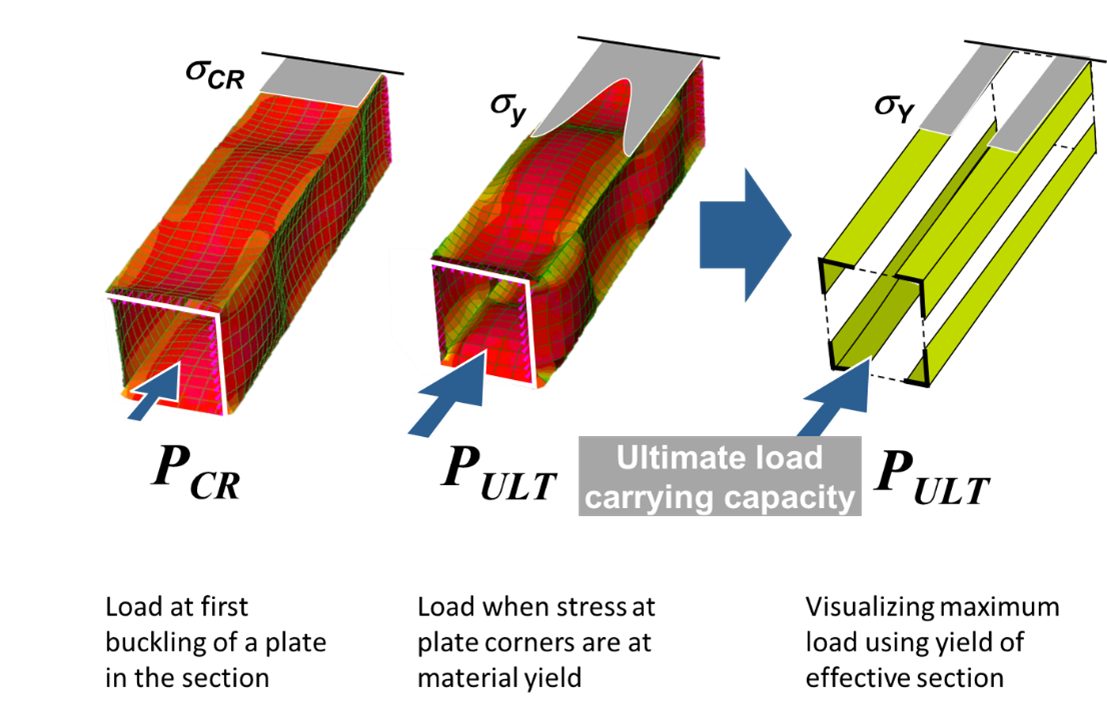
Figure 3: Concept of Effective Section.
Geometric Analysis of Sections – GAS2.0
Geometrical Analysis of Sections software determines the effective section for complex automotive sections. Figure 4 illustrates the GAS2.0 user interface. The user has the ability to construct sections or to import section data from a CAD system. Material properties for 63 steel grades are preloaded with the ability to also add user-defined steel grades. Two types of analysis are available. Nominal analysis, which provides classical area properties of the section, and Effective analysis which determines the effective section at material yield. Figure 5 summarizes both the tabular results and graphical results for each type of analysis.
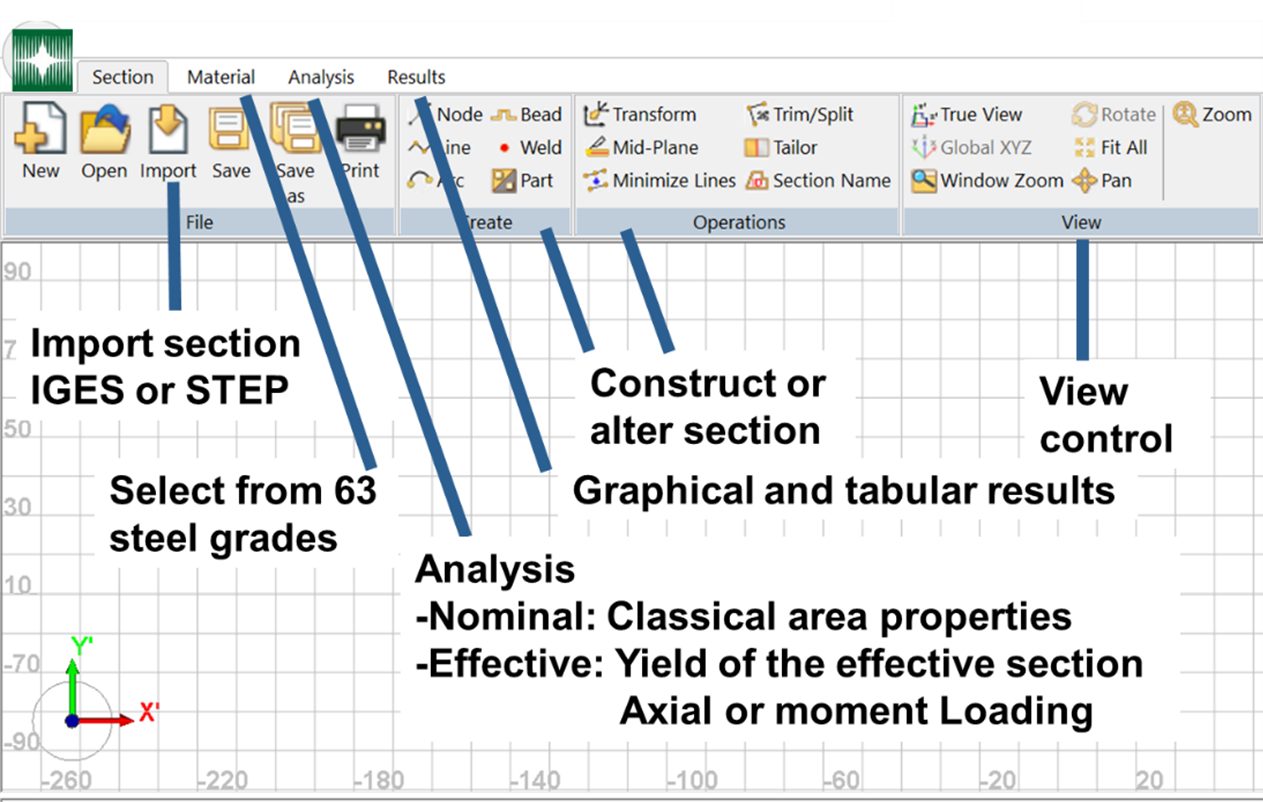
Figure 4: GAS2.0 User Interface.
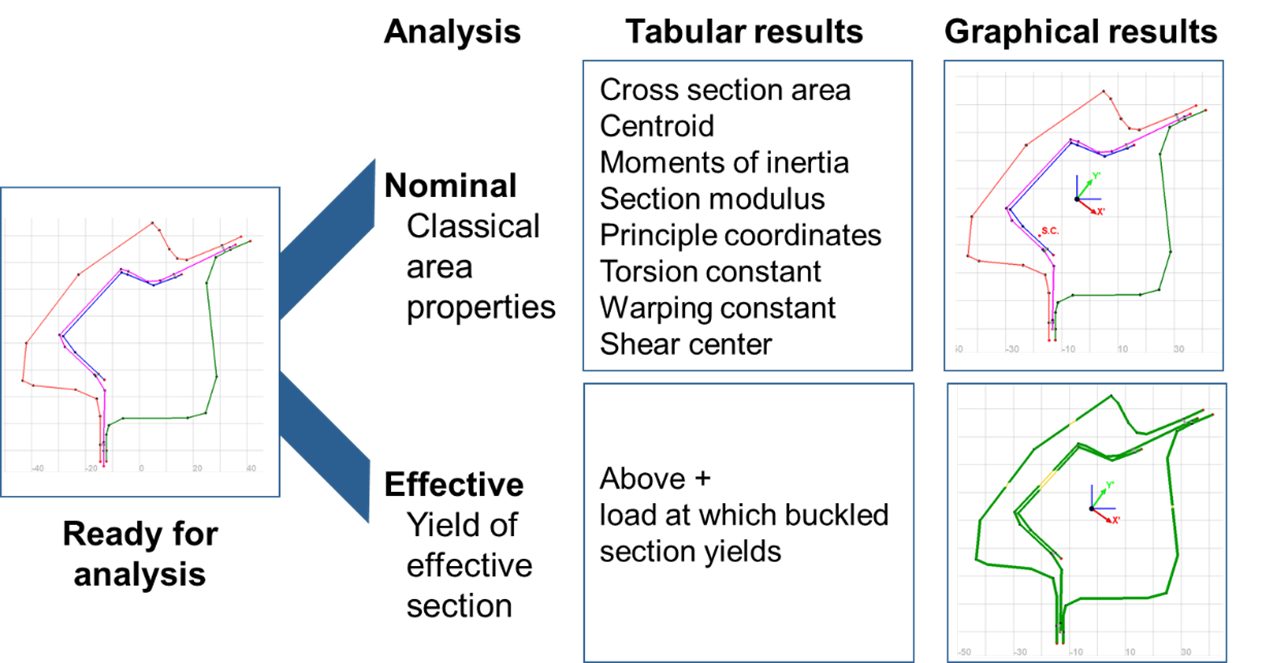
Figure 5. GAS2.0 Analysis Results.
Figure 6 illustrates an example of an Effective Analysis for a rocker section. In the graphical screen, the effective section is shown in green. Ideally, the whole section would be effective to fully use the materials yield capability. Also shown in the graphical screen are the section centroid, orientation of the principle coordinates, and stress distribution. In the right text box are tabular results. At the bottom of the tabular results is the axial load that causes this stress state and represents the ultimate load carrying ability of this section.
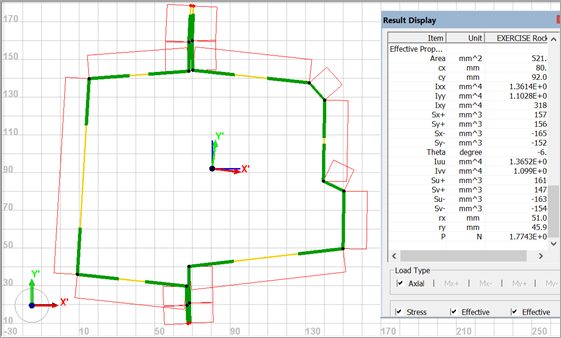
Figure 6: GAS2.0 Graphical Results.
It is clear that much of the material in the section of Figure 6 is not fully effective. GAS2.0 allows the user to conveniently modify the section. For example, in Figure 7 a bead has been added to the left side wall increasing its bulking resistance. Note that the side wall is now largely effective, and the ultimate load at the bottom of the text box has increased substantially.
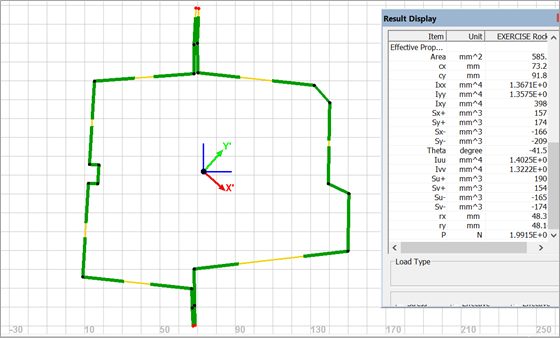
Figure 7: Improved Design Concept.
Role of GAS in the Design Process
GAS2.0 can play a significant role in early stage design, see Figure 8, by quickly creating initial designs which are more likely to function and to ensure that adequate package space is set aside for structure. This will result in fewer problems to fix later in the design sequence. During the detail design stage, GAS2.0 can supplement Finite Element Analysis by identifying problems earlier, and by screening design concepts for those with the greatest promise prior to more detailed analysis by FEA.
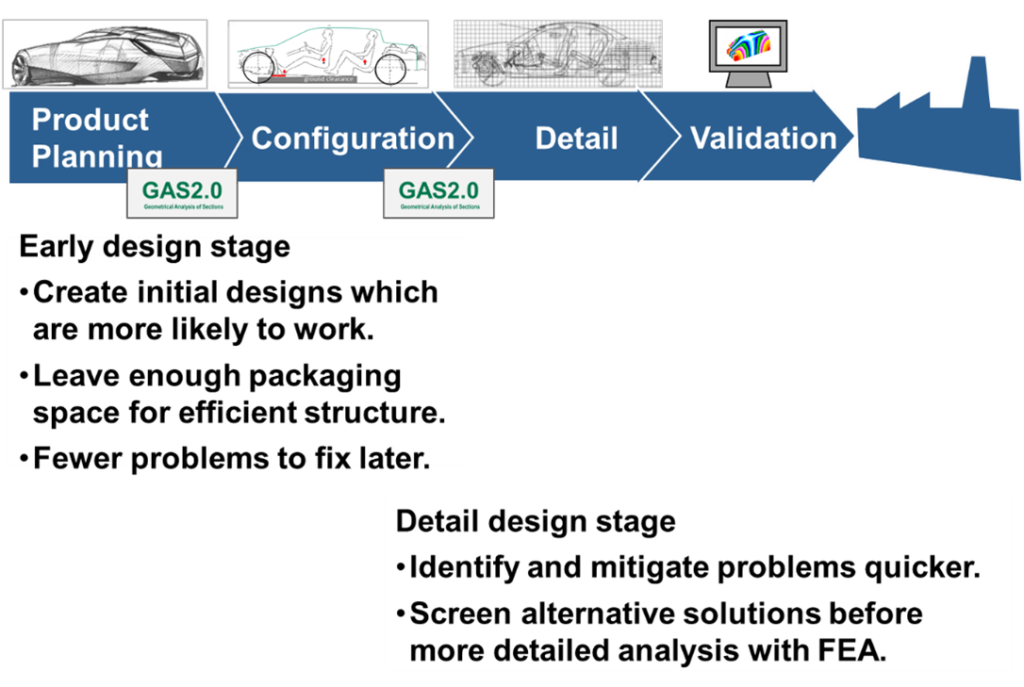
Figure 8: Role of GAS2.0 in Design Process.
GAS2.0 is available for free download at www.steel.org, Included in the resources at steel.org is an American Iron and Steel Institute introductory webinar conducted by Dr. Don Malen on 16 June 2020, as well as a number of GAS2.0 tutorials and training modules.