In order to reduce welding current and improve heat balance during resistance spot welding of aluminium alloy to steel, Qiu et al.Q-1, Q-2, Q-3, Q-4, Q-5 has investigated resistance spot welding of Aluminium/Steel with a cover plate on the aluminium alloy side. A 1 mm A5052 sheet and 1 mm cold-rolled steel (SPCC) sheet were resistance spot welded with a steel cover plate. The schematic diagram of the process is shown in Figure 1. The IMC layer composed of a tongue-like morphology of Fe2Al5 on SPCC side and needle-like morphology of FeAl3 on A5052 side.Q-1 With welding current of 9 kA, thickness of IMCs is higher than 1.5 µm at the center of the nugget and the thickness of IMCs gradually decrease with distance from the center and become discontinuous at the peripheral region (Figure 2). Peak load of cross-tension strength can be 0.77 kN with the welding current of 12 kA. A crack propagated at the peripheral of A5052 and through the reaction layer. Thus IMCs deteriorate the cross-tension strength as the IMC is thicker than 1.5 µm.Q-2 The tensile strength of resistance spot welded Aluminium/Steel was influenced by the fraction of discontinuous IMCs layer, and a strong Aluminium/Steel spot weld can be obtained with increasing discontinuous reaction layer fraction.Q-4
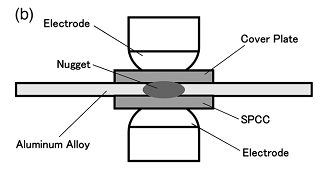
Figure 1: Schematic diagram showing resistance spot welding with a cover plate.Q-2
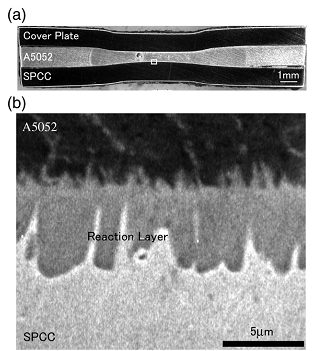
Figure 2: The cross-sectional macrostructure of spot weld joint (a) and SEM images of Al/steel interface.Q-2
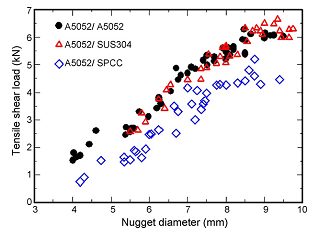
Resistance spot welding of 1mm A5052 to 1mm SUS 304 with a cover plate was investigated and compared to RSW of A5052/SPCC.Q-3 At all welding currents, the IMC layer is thinner at the A5052/SUS304 interface than at the A5052/SPCC interface, since Cr in SUS304 can reduce the growth rate of Fe2Al5 (Figure 3). A maximum tensile shear strength can be 6.5 kN for A5052/SUS304 which is comparable to A5052/A5052, which is higher than that of A5052/SPCC (4.68 kN) (Figure 4). However, interfacial fraction occurs at Al/steel interfaces in both cases.
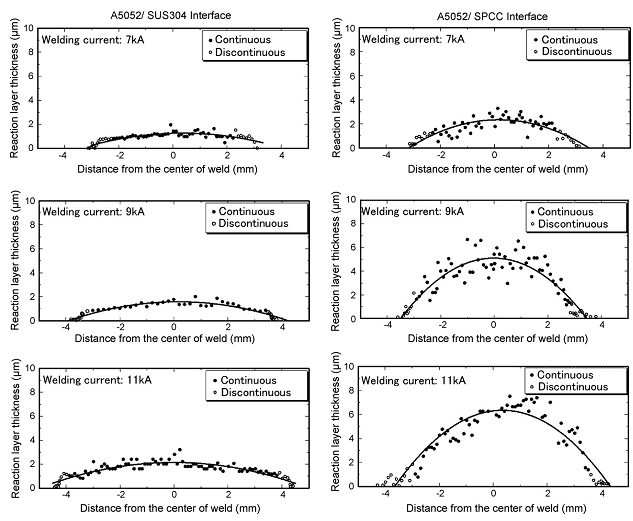
Figure 3: Distribution of intermetallic compound layer thickness at Al/steel spot weld interface.Q-3