Joining Dissimilar Materials
Multi-material design approach involves using High-Strength Steels and low-density materials, such as aluminium. The key idea is to utilize the right material for the right application in such a way that it should fulfill the service requirements and achieve mass efficiency at the same time. However, it is challenging to fully utilize multi-material design concepts due to joining issues.
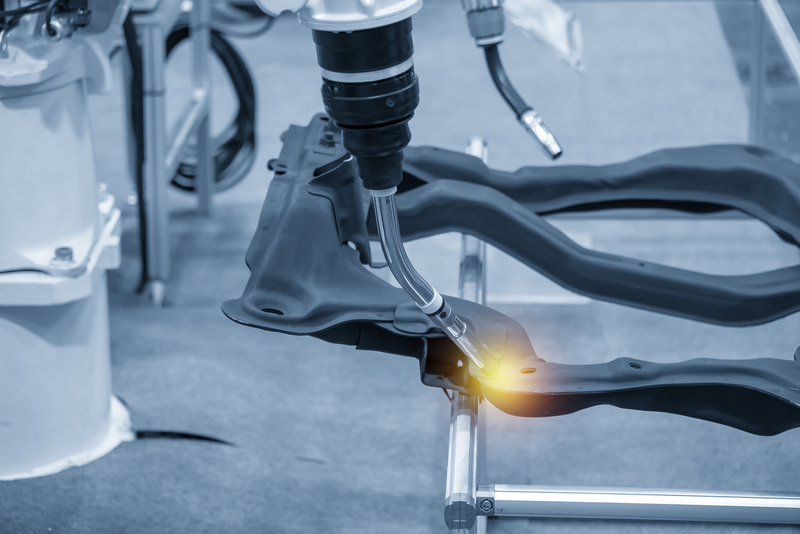
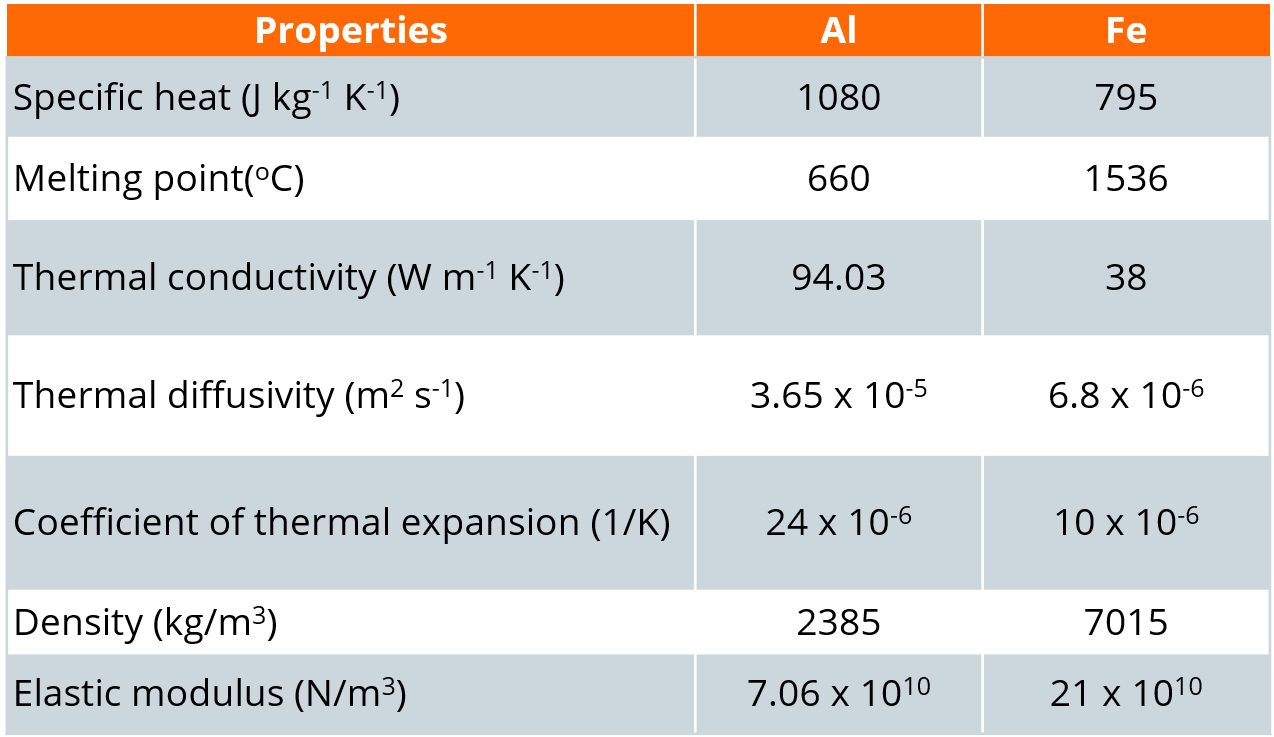
Joining is considered a backbone of any manufactured assembly, since the ultimate reliability and integrity of the manufactured product relies on these joints. Dissimilar materials are difficult to join due to the difference in the physical and thermal properties. For example, one of the most desired combinations is aluminium to steel joints, which is challenging due to the large mismatch in the mechanical properties as shown in Table 1. This Joining section is dedicated specifically to the key joining issues between aluminium and steel.
Currently there are three approaches to joining dissimilar materials: solid-state joining, partial solid-state joining and arc joining. During solid state welding, the peak temperature of the process remains below the melting temperatures of the materials to be joined. Examples include diffusion bonding, ultrasonic welding, magnetic pulse welding, friction stir welding and vaporizing foil actuator welding. In partial solid-state welding processes, the peak temperature goes beyond the melting temperature of one of the materials to be joined (e.g. arc brazing & resistance spot welding). The last process (arc welding) has a peak temperature above the melting temperature of both materials to be joined. Practically it is not used anywhere however, it can be utilized in certain applications where the mismatch between the physical properties of the materials to be joined is little.
Among various joining processes, resistance spot welding (RSW) is one of the most widely used joining process in the automotive and aerospace industry due to its ease of automation and high productivity. Browse the topics below to learn more about joining dissimilar materials.