RSW Modelling Process and Performance
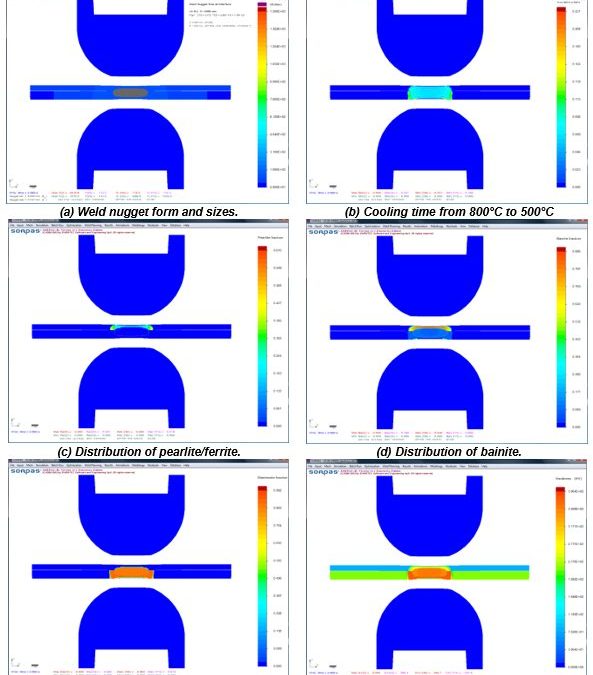
The advantages of numerical simulations for resistance welding are obvious for saving time and reducing costs in product developments and process optimizations. Today’s modeling techniques can predict temperature, microstructure, stress, and hardness distribution in the weld and Heat Affected Zone (HAZ) after welding. Commercial modeling software is available which considers material type, various current modes, machine characteristics, electrode geometry, etc. An example of process simulation results for spot welding of 0.8-mm DC 06 low-carbon steel to 1.2-mm DP 600 steel is shown in Figure 1. Obviously, this technique can apply to dissimilar thicknesses, material types, and geometries. Application of adhesives is also being used with these simulations. This simulation techniques are found to be very beneficial to predict vehicle crashworthiness as it can dramatically reduce the cost of crash evaluations.
You will find several articles in this section describing RSW modelling studies and procedures.
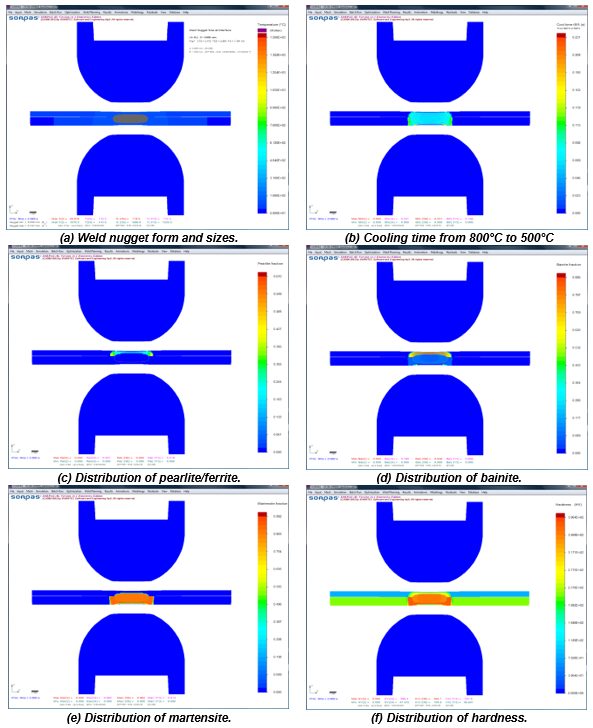
Figure 1: Simulation results with microstructures and hardness distribution for spot welding of 0.8-mm DC06 low-carbon steel to 1.2-mm DP 600 steel.Z-1