Key materials characteristics for formed parts include strength, thickness, and corrosion protection. Tailored products provide opportunities to place these attributes where they are most needed for part function, and remove weight that does not contribute to part performance.
Figure 1 highlights some of the areas within the body structure where companies have considered transitioning to welded tailored blanks. Other tailored products may be suitable in other areas.
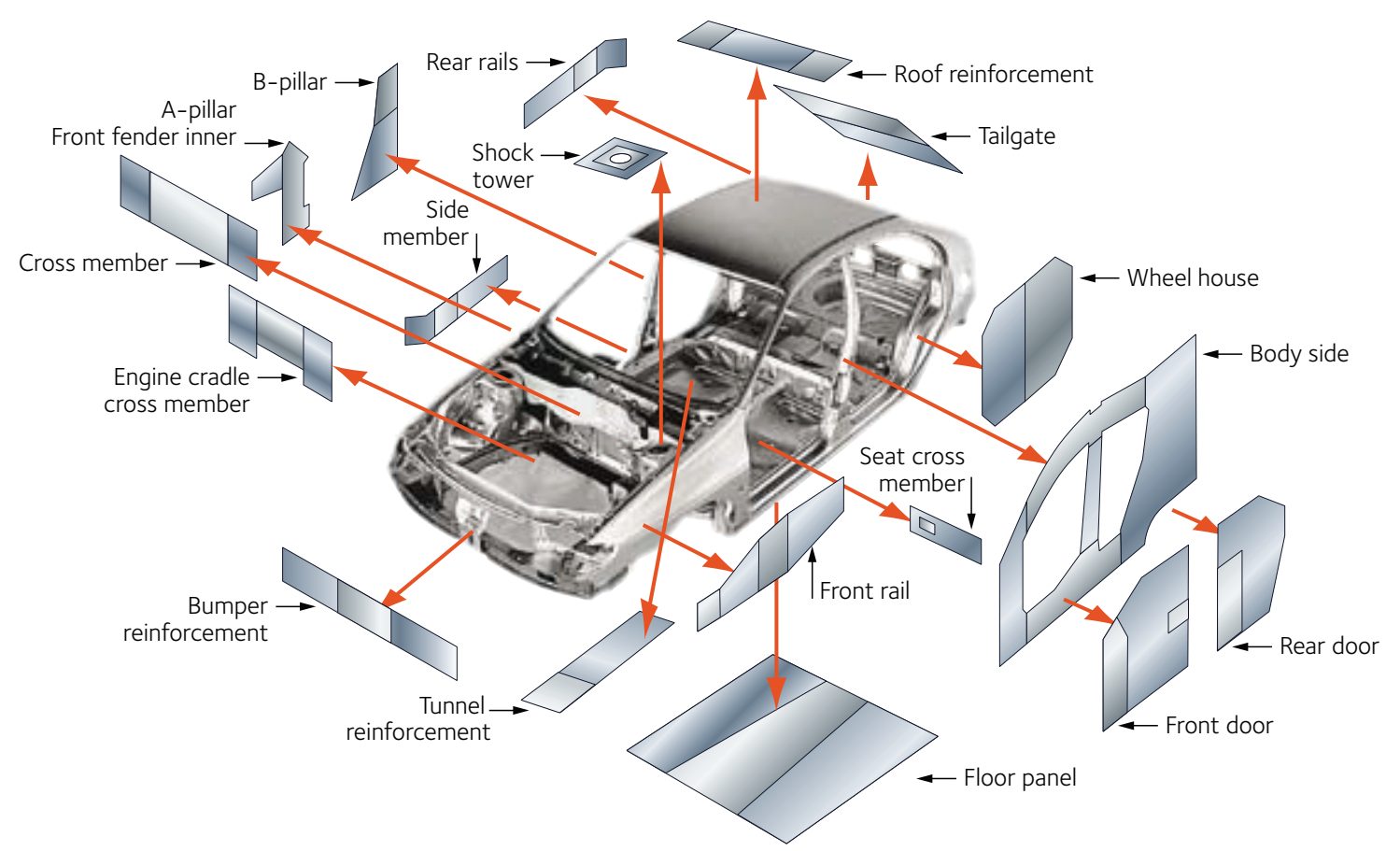
Figure 1: Applications suited for welded tailored blanks.A-31
Tailored products offer numerous advantages over the conventional approach involving the stamping and assembly of individual monolithic blanks which have a single grade, thickness, and coating, including:
Improved materials utilization
- Certain parts, like door rings, window frames, and door inner panels, have large cutout areas contributing to engineered scrap. Converting these to welded tailored blanks allows for optimized nesting of the individual components. Figure 2 presents an example of optimized nesting associated with body side aperture designs using a tailor welded blank. Reduced blank width requirements may allow for additional suppliers or use of master coils yielding slit mults. In the other extreme, blank dimensions larger than rolling mill capabilities are now feasible.
Elimination of reinforcement parts and reduced manufacturing infrastructure requirements
- In areas needing additional thickness for stiffness or crash performance, conventional approaches require stamping both the primary part and an additional smaller reinforcement and then spot welding the two parts together. The tailored product directly incorporates the required strength and thickness. Compared with a tailored product, the conventional approach requires twice the stamping time and dunnage, creates inventory, and adds the spot welding operation. Tolerance and fit-up issues appear when joining two formed parts, since their individual springback characteristics must be accommodated.
Part consolidation
- Similar to the benefits of eliminating reinforcements, tailored products may combine the function of what would otherwise be multiple distinct parts which would need to be joined.
Weight savings
- Conventional approaches to body-in-white construction requires individual parts to have flat weld flanges to facilitate spot welding. Combining multiple parts into a tailored product removes the need for weld flanges, and their associated weight.
Improved NVH, safety, and build quality
- Joining formed parts is more challenging than joining flat blanks first and then stamping. Tailored products have better dimensional integrity. Elimination of spot welds leads to a reduction in Noise, Vibration, and Harshness (NVH). A continuous weld line in tailored products means a more efficient load path.
Enhanced engineering flexibility
- Using tailored products provides the ability to add sectional strength in precise locations to optimize body structure performance.
Easily integrated with advanced manufacturing technologies for additional savings
- Tailored products incorporated into hot stamping or hydroforming applications magnify the advantages described here, and open up additional benefits.
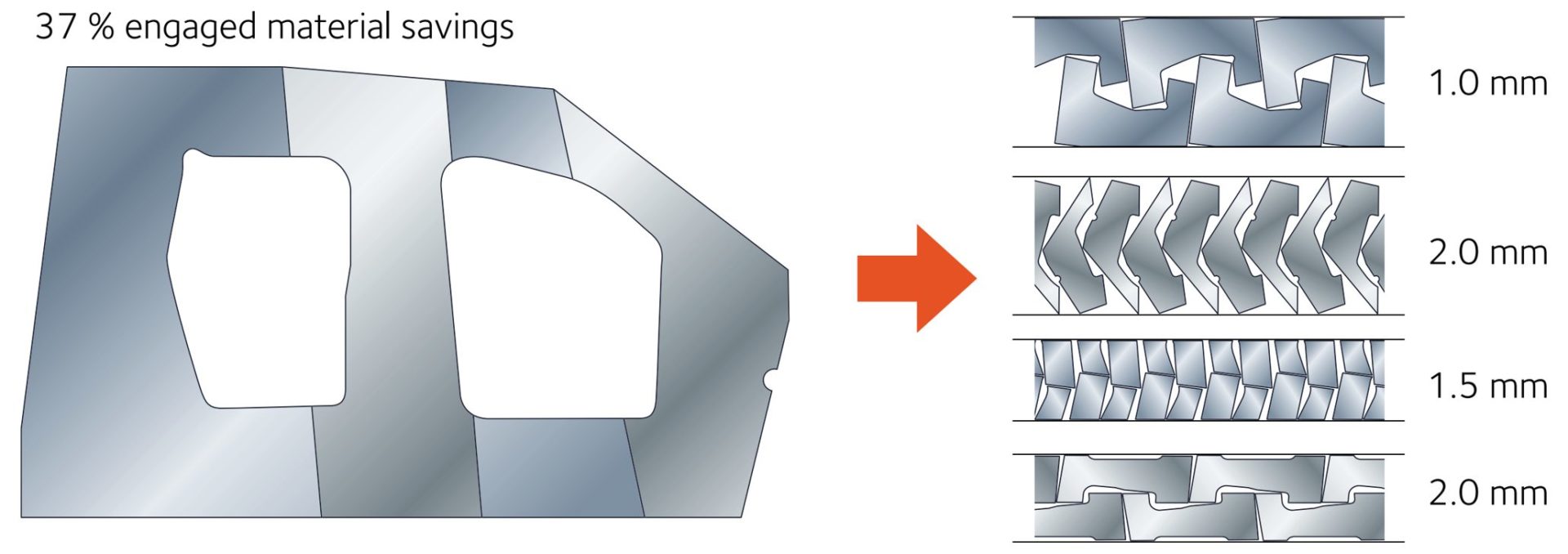
Figure 2: Nesting optimization dramatically reduces engineered scrap.A-31
To learn more about the different types of Tailored products, read the full article here.
TEASER!: A future post will highlight how these tailored products are applied to press hardening steels to create a single component having strength levels tuned to the needs of each segment of the body structure. Stay tuned!