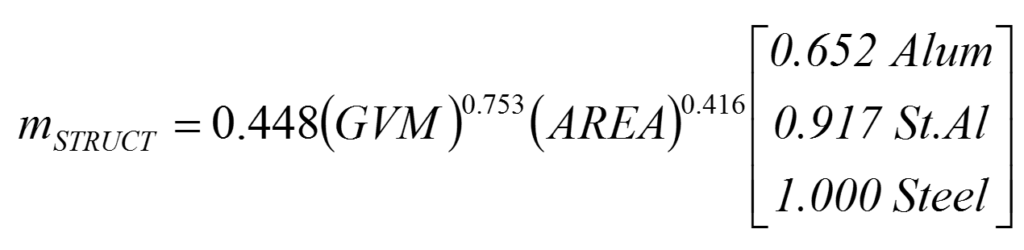
Blog, main-blog
In static or dynamic conditions, the spot weld strength of Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS) may be considered as a limiting factor. One solution to improve resistance spot weld strength is to add a high-strength adhesive to the weld. Figure 1 illustrates the strength improvement obtained in static conditions when crash adhesive (in this case, Betamate 1496 from Dow Automotive) is added. The trials were performed with 45-mm-wide and 16-mm adhesive bead samples.
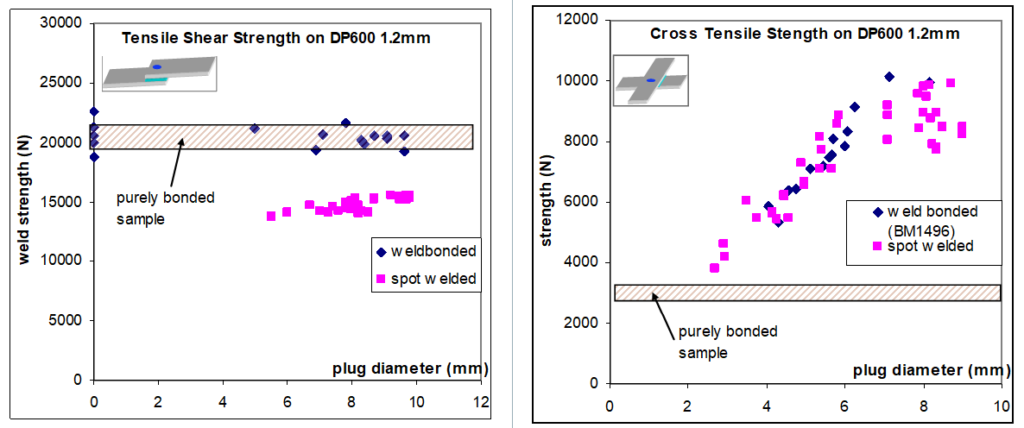
Figure 1: Tensile Shear Strength and Cross Tensile Strength on DP 600.A-16
Another approach to improve the strength of welds is done by using laser welding instead of spot welding. Compared to spot welding, the main advantage of laser welding, with respect to the mechanical properties of the joint, is the possibility to adjust the weld dimension to the requirement. One may assume that, in tensile shear conditions, the weld strength depends linearly on the weld length as indicated in the results of a trial A-16, shown in Figure 2.
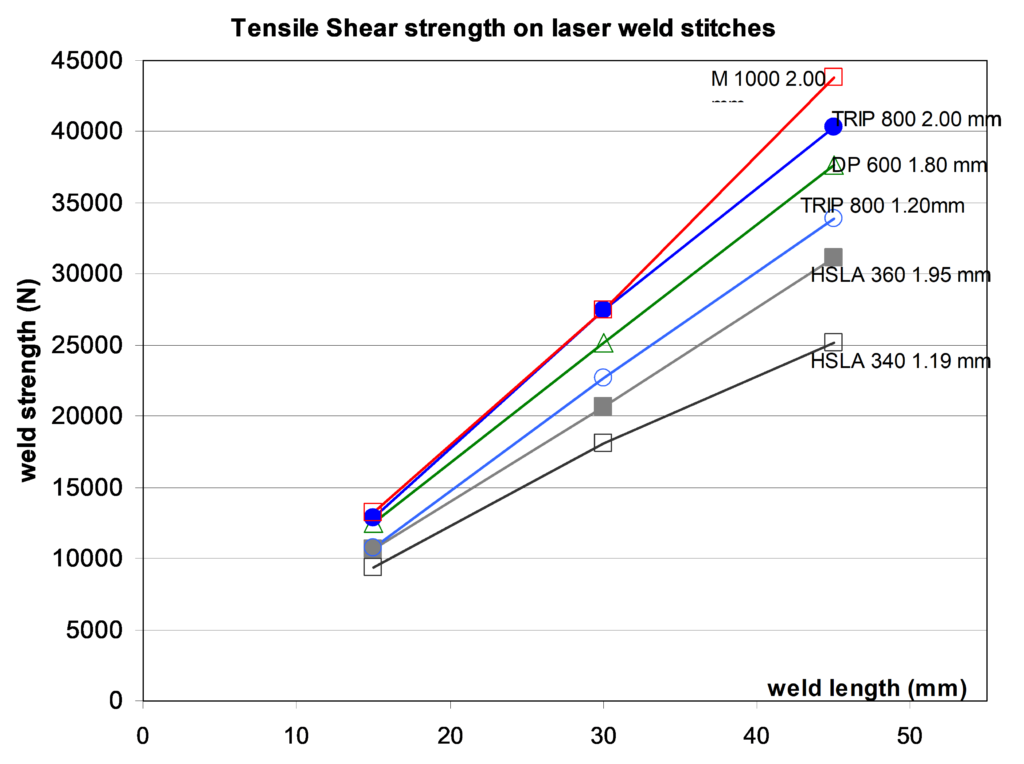
Figure 2: Tensile-shear strength on laser weld stitches of different length.A-16
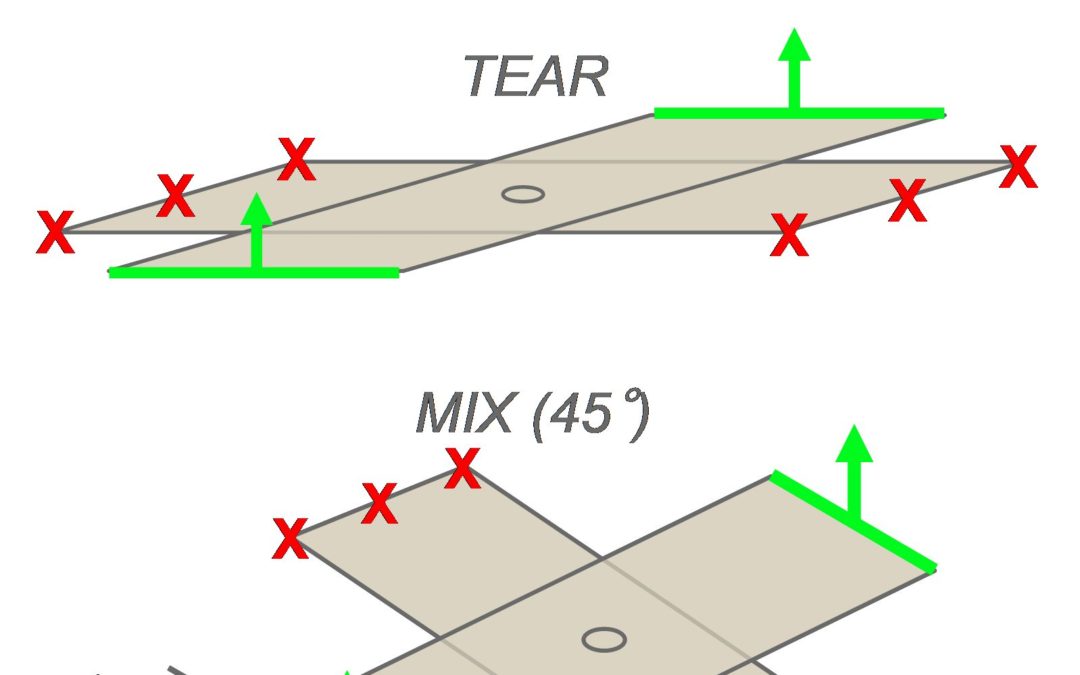
However, a comparison of spot weld to laser weld strength cannot be restricted to the basic tensile shear test. Tests were also conducted to evaluate the weld strength in both quasi-static and dynamic conditions under different solicitations, on various AHSS combinations. The trials were performed on a high-speed testing machine, at 5 mm/min for the quasi-static tests and 0.5 m/s for the dynamic tests (pure shear, pure tear or mixed solicitation, as shown in Figure 3). The strength at failure and the energy absorbed during the trial were measured. Laser stitches were done at 27mm length. C- and S-shape welds were performed with the same overall weld length.
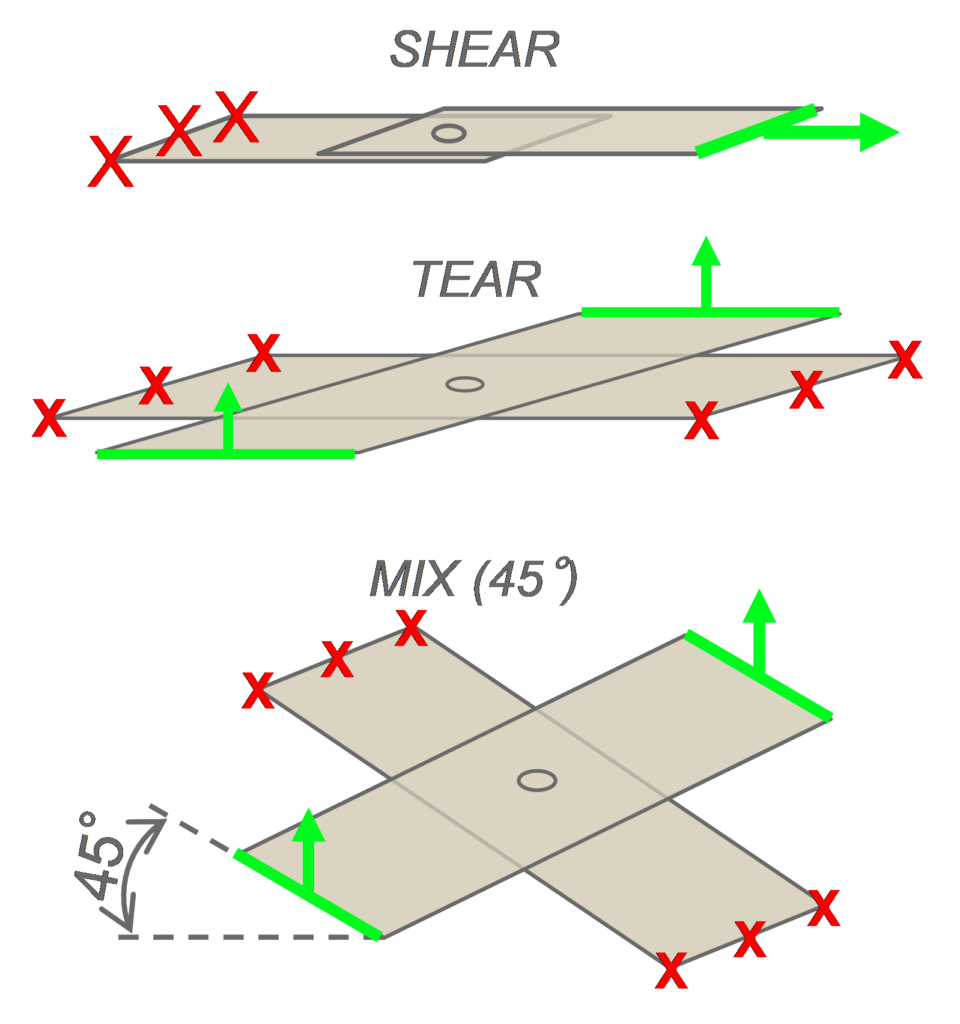
Figure 3: Sample geometry for quasi-static and dynamic tests.A-16
The weld strength at failure is described in Figure 4, where major axes represent pure shear and tear (Figure 4). For a reference spot weld corresponding to the upper limit of the weldability range, globally similar weld properties can be obtained with 27mm laser welds. The spot weld equivalent length of 25-30 mm has been confirmed on other test cases on AHSS in the 1.5- to 2 mm thickness range. It has also been noticed that the spot weld equivalent length is shorter on thin mild steel (approximately 15-20 mm). This must be considered when shifting from spot to laser welding on a given structure. There is no major strain rate influence on the weld strength; the same order of magnitude is obtained in quasi-static and dynamic conditions.
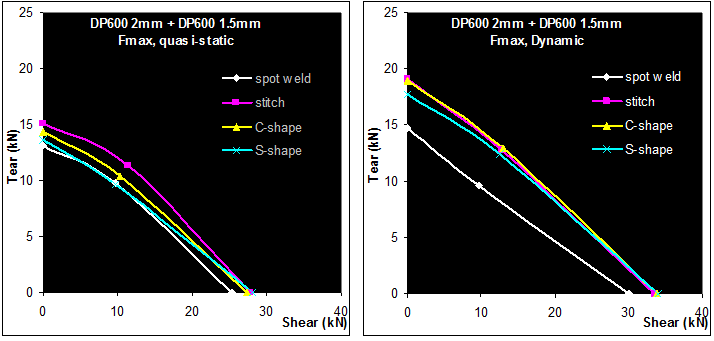
Figure 4: Quasi-static and dynamic strength of welds, DP 600 2 mm+1.5 mm.A-16
The results in terms of energy absorbed by the sample are seen in Figure 5. In tearing conditions, both the strength at fracture and energy are lower for the spot weld than for the various laser welding procedures. In shear conditions, the strength at fracture is equivalent for all the welding processes. However, the energy absorption is more favorable to spot welds. This is due to the different fracture modes of the welds; for example, interfacial fracture is observed on the laser welds under shearing solicitation. Even if the strength at failure is as high as for the spot welds, this severe failure mode leads to lower total energy absorption.
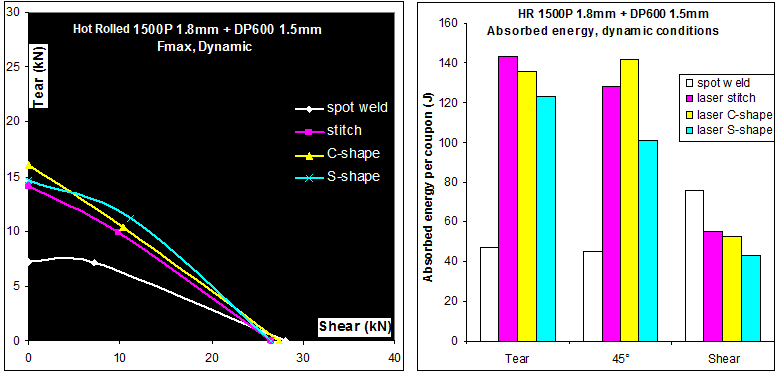
Figure 5: Strength at fracture and energy absorption of Hot Rolled 1500 1.8-mm + DP 600 1.5-mm samples for various welding conditions.A-16
Figure 6 represents the energy absorbed by omega-shaped structures and the corresponding number of welds that fail during the frontal crash test (here on TRIP 800 grade). It appears clearly that laser stitches have the highest rate of fracture during the crash test (33%). In standard spot welding, some weld fractures also occur. It is known that AHSS are more prone to partial interfacial fracture on coupons, and some welds fail as well during crash tests. By using either Weld-Bonding or adapted laser welding shapes, weld fractures are mitigated, even in the case of severe deformation. As a consequence, higher energy absorption is also observed.
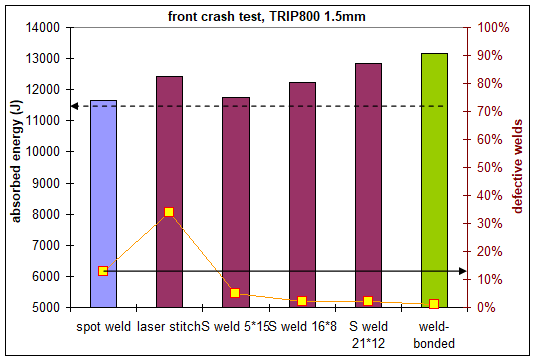
Figure 6: Welding process and weld shape influence on the energy absorption and weld integrity on frontal crash tests.A-16
Up to a 20% improvement can be achieved in torsional stiffness, where the best results reflected the combination of laser welds and adhesives. Adhesive bonding and weld- bonding lead to the same stiffness improvement results due to the adhesive rather than the additional welds. Figure 7 shows the evolution of the torsional stiffness with the joining process. Optimized laser joining design leads to the same performances as a weld bonded sample in fracture modes, shown in Figure 8.
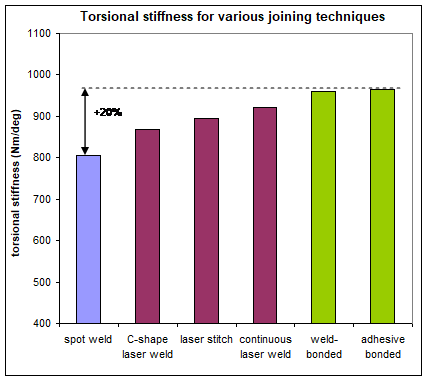
Figure 7: Evolution of the torsional stiffness with the joining process.A-16
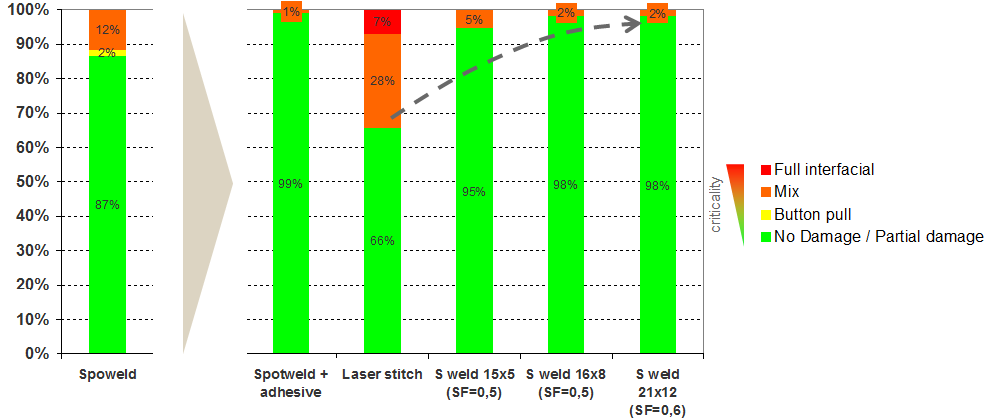
Figure 8: Validation test case 1.2-mmTRIP 800/1.2-mm hat-shaped TRIP 800.
Top-hat crash boxes were tested across a range of AHSS materials including DP 1000. The spot weld’s energy absorption increased linearly with increasing material strength. The adhesives were not suitable for crash applications as the adhesive peels open along the entire length of the joint. The weld bonded samples perform much better than conventional spot welds. Across the entire range of materials there was a 20-30% increase in mean force when weld bonding was used; the implications suggesting a similarly significant improvement in crash performance. Furthermore, results show that a 600 MPa weld bonded steel can achieve the same crash performance as a 1000 MPa spot-welded steel. It is also possible that some down gauging of materials could be achieved, but as the strength of the crash structure is highly dependent upon sheet thickness, only small gauge reductions would be possible. Figure 9 shows the crash results for spot-welded and weld bonded AHSS.
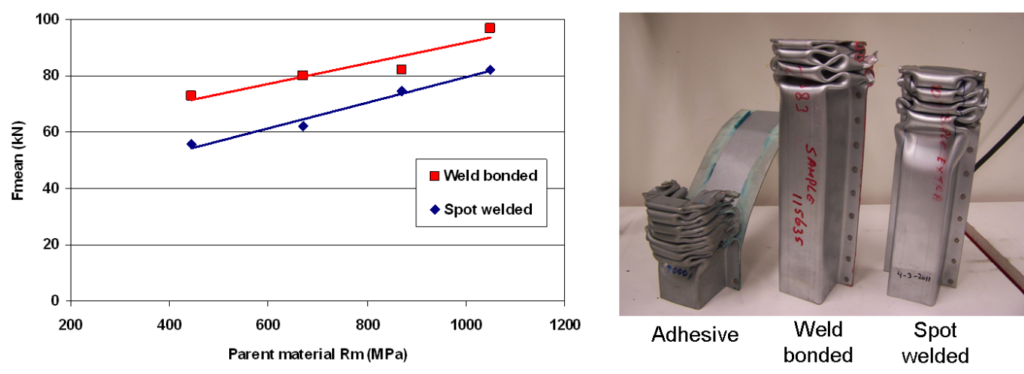
Figure 9: Crash results for spot-welded and weld bonded AHSS.
Blog, main-blog
Forty years ago, the metal forming community needed to figure out how to stamp a new exotic family of steels making inroads into automotive body construction. These grades, called High Strength Low Alloy steels, were much stronger than the commonplace mild steels, and were more formable than the high-strength options available at that time. Initially, only a few steelmakers were able to offer these new grades, but over time more companies added the equipment and know-how necessary to support their customers with these products. Automakers and their supply chain stampers needed to adapt as an increasing number of parts transitioned to HSLA steels.
Fast-forward a few decades, and metal formers are facing similar challenges. Successful forming and joining of Advanced High-Strength Steels is made easier with processes that are tuned to work with the characteristics associated with these alloys. One such technique to improve formability is to employ Active Binder Force Control.
In conventional stamping, a draw ring applies pressure around the binder in order to control the sheet metal flow into the cavity. The ring may be referred to as a binder plate, draw pad, pressure pad, or blank holder. Creating the restraining force typically is done with urethane springs, coil springs, gas springs (like air or nitrogen), or press cushion systems actuated by gas or hydraulic cylinders.
Where the traditional approach applies binder pressure uniformly throughout the press stroke, modern stamping presses can be equipped with cushions having multipoint-control systems (see Figure 1 example). The associated pressure profile can be adjusted around the panel and throughout the stroke to optimize metal flow, prevent splits and wrinkles, and minimize thinning.
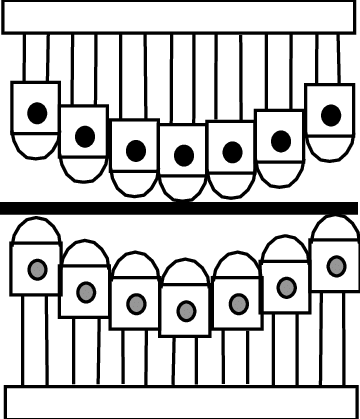
Figure 1. An Example of Multi-Point Press Forming Method.P-31
Incorporating Active Binder Control capabilities has several benefits for the press shop, panel quality, and product design, including:
- A segmented blankholder combined with individually programmable hydraulic cylinders, sometimes called a flexible binder, allows for precise control of one segment independent of the others.
- Pulsating blank holder force has been shown to reduce press tonnage requirements and increase metal flow, with the frequency and amplitude being key variables that must be adjusted based on the grade and thickness of interest.
- Pre-acceleration of the cushion reduces shock loading, which minimizes the press-damaging snap-through loads associated with reverse tonnage.
The merits of a variable blank holder force on AHSS springback were documented in a 2004 conference paper.M-63 With the traditional constant binder force approach, springback in the form of side-wall curl was seen in parts made from either a DP590 grade or a mild steel grade used as a control. Increasing the constant binder force helped to reduce springback in the mild steel part.
In Figure 2, CBF reflects tests conducted with constant binder force. VBF-LH and VBF-MLH reflect variable binder force tests conducted with a low-high force profile sequence and a medium-low-high force profile, respectively.

Figure 2: Variable Binder Force Reduces Springback.M-63
By employing a variable binder force, springback of both the mild steel and the DP 590 material was substantially reduced. Employing either variable binder force approach reduced the thinning from forming the DP 590 material, resulting in a more uniform strain distribution across the entire channel profile (Figure 3).
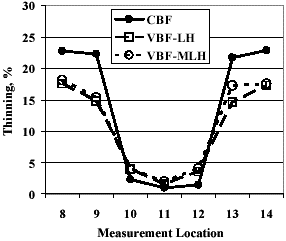
Figure 3: Uniform Strain Distribution Achieved with Variable Binder Force.M-63
More recently, a presentation from 2018 showed CP 800 panel quality improvements associated with variable blank holder force capabilities.D-33 Panel results from a constant binder force of 300 kN and 400 kN are shown in Figures 4 and 5, respectively. Both exhibit severe wrinkling in the flange. Applying 500 kN binder force was not feasible due to exceeding the press tonnage curve limits throughout the stroke.

Figure 4: CP800 Panel Formed with Constant Binder Force of 300 kN, and Associated Close-Up of Flange.D-33

Figure 5: CP800 Panel Formed with Constant Binder Force of 400 kN, and Associated Close-Up of Flange.D-33
Figure 6 shows the panel produced with a variable binder force. The chosen profile fit within the press tonnage requirements and minimized wrinkles.

Figure 6: CP800 Panel Formed with Variable Binder Force Ramping from 300 kN to 600 kN, and Associated Close-Up of Flange.D-33
Active drawbead control is an offshoot of these techniques, allowing for the magnitude and timing of drawbead engagement to be optimized for the requirements of each part. A description of using stake beads to minimize springback is available in the Springback article – active drawbead control is one approach to actuate beads.
The initial laboratory studies relating to active binder force control go back nearly 20 years ago. In the coming years, more information will enter the public domain on how metal formers are using these concepts in production. When you look to purchase a servo press, be sure to ask your press manufacturer about programmable cushions.
Blog, main-blog
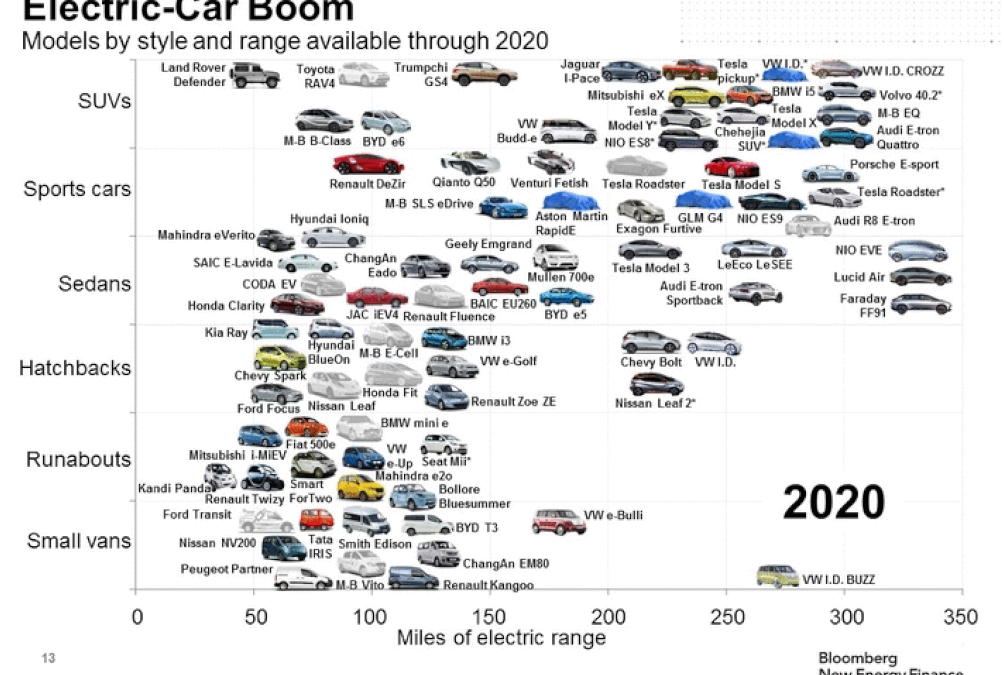
Several recent studies are forecasting that; “Within the next 10 to 15 years, urban transportation will be dominated by Electric and Automated vehicles”.B-50 Meaning most of us will be driving Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) in the not-distant future. In 2011, just eight years ago, there were only three BEVs on the market with 70 to 80 miles range on a single charge. These were the first generation BEVs. Since then, the number of EVs on the market has increased, with significant improvements in range (now approaching 300 miles). BEV 2020 vehicles cover all current segments, from small cars to SUV’s and trucks (Figure 1). These vehicles will be available from most OEMs as well as several new start-up companies. The construction material for body structures of these vehicles is predominantly steel, while some of the premium vehicles ($60,000 to $100,000) are aluminium. And the prevailing OEM message seems to be “anything TESLA can do, we can do better”.
So how will this change the vehicle body structure design, choice of construction material, its implications for manufacturing and assembly, and ultimately, the impact on automotive steel?
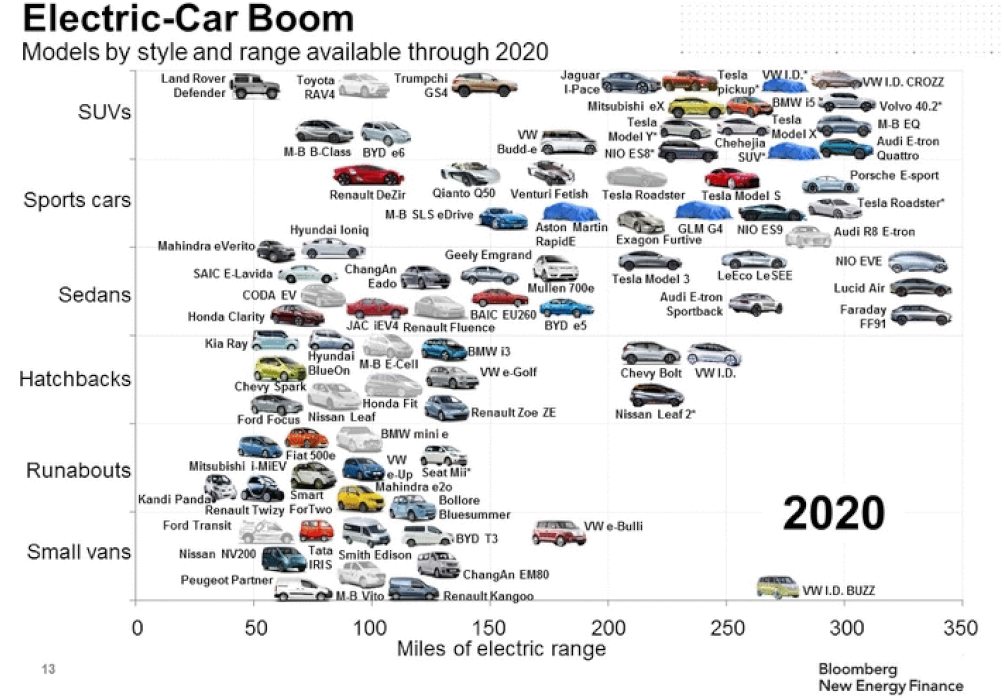
Figure 1: Electric Vehicle Boom – Models by Style and Range Available Through 2020.B-50 CHART SUMMARY: a) Covers all current segments, b) Structures predominantly Steel, c)Some premium vehicles highlight Aluminium, d)Products from most OEMs as well as several new start-up companies.
The driver for this electrification boom is increasing affordability. The upfront cost of BEVs will become competitive on an unsubsidized basis starting in 2024.F-38 By 2030 in the U.S., almost all light duty vehicle segments will reach cost parity as battery prices continue to fall.B-73 Forecasters, such as McKinsey, Morgan Stanley and Bloomberg, predict that about half of all new vehicle production will be electric somewhere between 2035 and 2040. However, Tesla’s CEO Elon Musk’s prediction is much more aggressive. He expects more than half of new vehicles in the U.S. will be electric within the next 10 years, roughly 10 to 15 years ahead of most other predictions.
The Main Drivers of BEV Cost Reduction
- Lithium-ion battery prices have fallen 75% since 2013, hitting $176/kWh in 2018 (Figure 2). Industry-wide prices fell due to the adoption of new cell designs and the availability of higher energy-density cathodes. Prices are expected to drop further in coming years to below $100 per kWh. Besides the reduction in cost, packaging efficiency and the cell energy density also is improving.
- Package space required by other BEV powertrain systems also is being optimized, e.g., motor, transmission, differential and power electronics. This is yielding significant weight and cost reductions, which are then directly reinvested into lower-cost structural materials, such as Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS) versus higher cost Aluminium, to keep the overall price of the vehicle low.
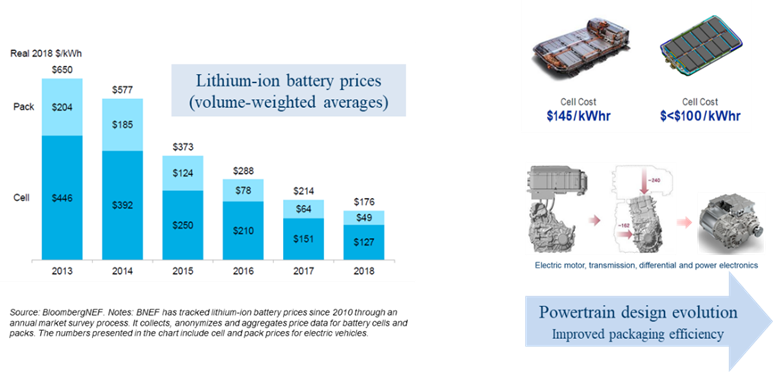
Figure 2: BEV Price Parity with Gas-powered Cars by 2024 – Main Drivers.B-74
BEV to ICE Vehicle Structural Differences and Advantages for Steel
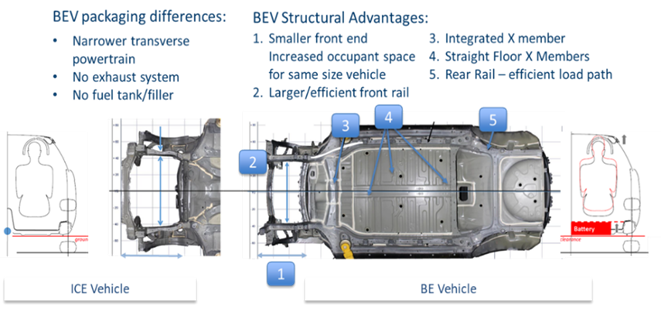
Figure 3: BEV to ICE Vehicle Structural Differences.M-64
BEV packaging differences compared with ICE Vehicles are shown in Figure 3, and include:
- Narrower and compact transverse electric powertrains, leading to shorter front end, with increased occupant space for same size vehicle and larger/efficient front crash rails.
- Lack of an exhaust system eliminates the need for the tunnel, allowing straighter/ efficient cross-members.
- No fuel tank/filler leads to more efficient rear rail load path.
- High voltage electric powertrain and large (300 litres, 500 kg) under-floor battery pack crash protection requirements result in higher safety requirements for BEV front and side structures.
- Safety. The BEV body structure load path requirements are ideal for AHSS application. The floor cross members, without the presence of the tunnel, are straight and can use very high-strength martensitic roll formed sections. Cross members can be stamped from 3rd Generation Steels offering Giga-Pascal strength and over 20% elongation. For frontal crash load management and to minimize passenger/battery compartment intrusions for increased safety, 3rd Generation steels offer the most mass/cost efficient solution. The very high strengths offered by AHSS and UHSS for the safety-critical structural members such as the rocker, rails, cross members and pillars, greatly enhance the required protection of the BEV powertrain and high energy/voltage battery systems. The battery enclosure construction greatly benefits from AHSS usage, providing protection from road-debris impacts from below the vehicle, along with fire protection into the passenger compartment. Advanced steels also enable reduced section sizes for the occupant compartment, required for improved panoramic visibility, without compromising occupant safety and comfort.
- Cost. For widespread adoption of BEVs to occur, the overall cost of the vehicle must be affordable, and its range must be above the ‘range anxiety limit’ of most drivers. Various surveys indicate this range to vary greatly from 75 miles to over 400 miles. Using steel for the vehicle structure leads to the lowest cost BEV, just as with ICE-based vehicles. The vehicle range can be increased through lightweighting and/or by increasing the size of the battery; a cost comparison of these two options is shown in Figure 4. With battery cost reduction approaching $100 per kWh, lightweighting is cost effective at approximately US$2.00 per kg saved. Lightweighting is still very important and the latest steel grades, in particular 3rd Generation steels, offer the most cost-effective lightweighting option. In comparison, if we consider lightweighting with aluminium, the cost is typically in the order of US$6.00 per kg saved. This could be cost effective if the battery cost is over $250 per kWh, which was the case a decade ago. We can see the evidence of this in OEM decisions at that time. For example, the 2011 Nissan Leaf BEV closures were aluminium; but the latest 2019 Nissan leaf BEV closures are steel.
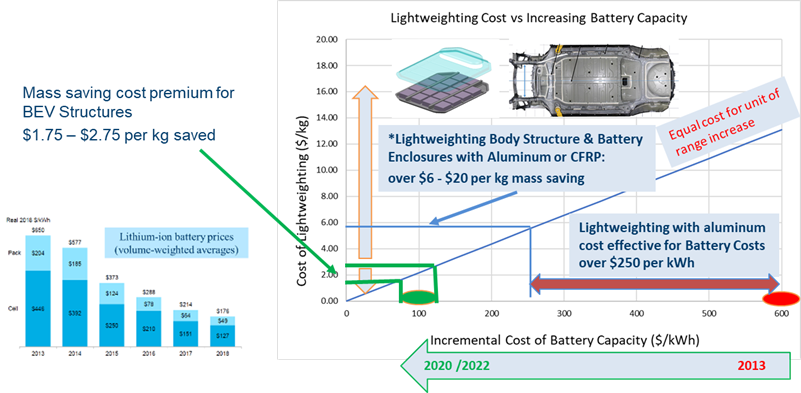
Figure 4: BEV Range Increase – Lightweighting Cost versus Battery Cost 2020 – 2022.M-64
Battery Electric Vehicles – Boom or Bust for AHSS?
For the increased safety required for BEVs to protect the high voltage systems, the structural load paths are ideally suited for the Giga Pascal level strengths offered by AHSS and UHSS. The Battery Enclosure structure offer an additional 85 kg per vehicle opportunity, an increase of approximately 10% sheet metal over ICE vehicles. Also, using advanced steels the BEV structure can take full advantage of well-established body shop practices for manufacturing and assembly, such as stamping, roll forming and spot welding. With future increased focus on BEV affordability, safety and sustainability, steel offers the best solutions and flexibility to address these key challenges.

Blog
We’ve been monitoring the evolution of vehicle legislation in the world closely, advocating for life cycle thinking to be considered for the next generation of regulations. The European Union has been actively pursuing Post 2020 regulations, looking hard at CO2 emissions reduction. On 15 May 2019, the new EU CO2 emission legislation for cars and vans for the post-2021 period entered into force, with the objective of contributing to decarbonisation and modernisation of Europe’s road transport sector in line with the EU’s commitments under the Paris International Climate Agreement. The main instrument to achieve this is a further reduction of tailpipe CO2 emissions from new cars by 37.5% by 2030 compared with the 2021 baseline as well as providing incentives to car manufacturers to sell more low-emission vehicles (<50gCO2/km) in the EU.
The direction of EU policy appears clear: cars need to emit less CO2. Others are questioning the focus on emissions reduction in the use phase of a vehicle and whether this will result in overall emissions savings. In fact, improvements in the driving phase could be cancelled out by increased emissions from the production and later the recycling of the vehicle as manufacturers turn to alternative materials and powertrains that could be more energy intensive to produce.
So, what is the solution?
Perhaps it is already in the recently adopted EU. The legislative text is for all intents and purposes a continuation of the existing CO2 emission legislation with more stringent tailpipe-based targets and verification. Yet it features one notable new element: the idea of reporting on the life cycle emissions of cars.
Article 7 – Monitoring and reporting of average emissions
10. The Commission shall no later than 2023 evaluate the possibility of developing a common Union methodology for the assessment and the consistent data reporting of the full life-cycle CO2 emissions of passenger cars and light commercial vehicles that are placed on the Union market. The Commission shall transmit to the European Parliament and to the Council that evaluation, including, where appropriate, proposals for follow-up measures, such as legislative proposals.
By 2023, the European Commission is tasked with assessing the feasibility of creating an EU methodology for harmonised and consistent reporting of full vehicle life cycle CO2 emissions.
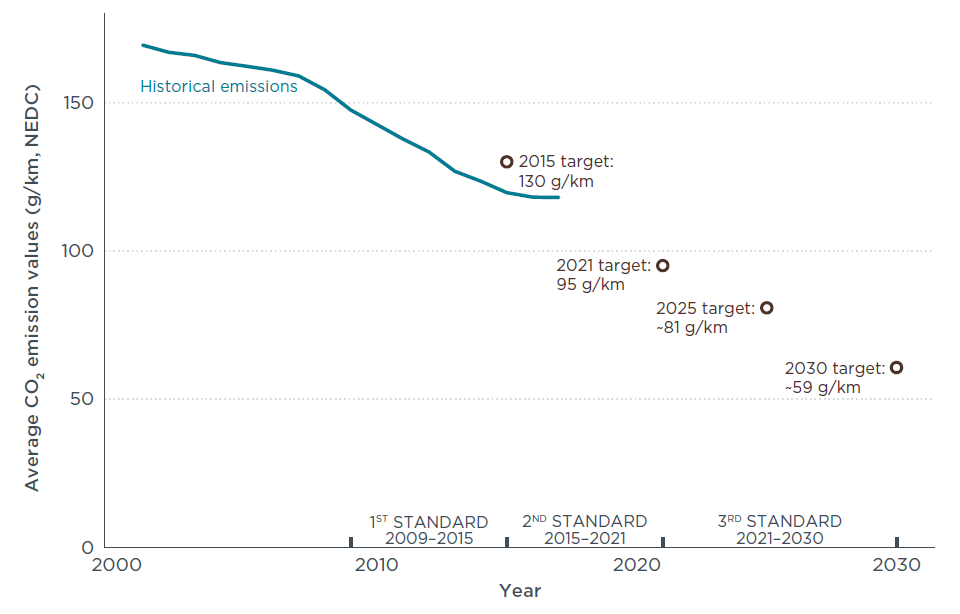
Figure 1: Average historical CO2 emission values and adopted CO2 standards for new passenger cars in the EU. All CO2 values refer to New European Driving Cycle (NEDC) measurements. Source: ICCT
With a reporting framework of this kind, regulators could better anticipate the impact of changes in the vehicle fleet on overall emissions and identify the appropriate policy instruments, thereby being able to future-proof the legislation.
Going forward, the European Commission is expected to undertake a feasibility study to identify possible ways to measure vehicle life cycle emissions in a consistent and harmonised way. The conclusions of this work and any possible recommendations for implementing the methodology into EU law would be part of a report to the European Parliament in time for a review of the Regulation by 2023.
As life cycle assessments are already used by a wide range of stakeholders in the automotive sector, it will also be up to them to contribute to this work and help ensure future debates on the best way to decarbonise the EU road transport sector can draw on their experience.

Blog, main-blog
Here at WorldAutoSteel, we have been studying the changes in the automotive industry for several years, focusing particularly on ride sharing, autonomous, electric vehicles and steel’s role in that marketplace. George Coates, Technical Director for WorldAutoSteel and The Phoenix Group, has been leading that effort and today contributes an article on the disruption of future mobility to the industry and the great opportunities we see for steel in meeting the challenges providers will face. We hope you enjoy the read, and we welcome your thoughts and comments. What changes and impacts do you envision for vehicle manufacture? How do you feel about the world of autonomy?
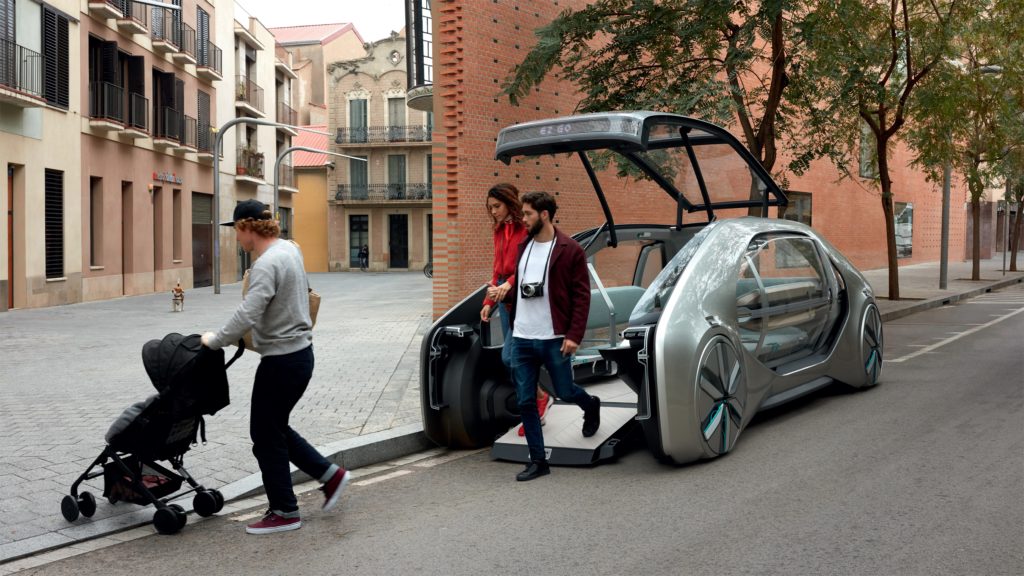

Renault’s Future Mobility concept, the E-Z Go
We’re approaching a critical milestone in automotive history when what we know as normal is about to change significantly. Future Mobility describes the revolution that’s already begun. We’re rethinking transportation from the movement of a vehicle to a more efficient concept for moving people and things. We’re about to discover the social advantages of connected, autonomous, shared and electric vehicles. And we’re completely changing the way we view transportation.
By 2030, electric vehicles (EVs) will be mainstream—not just within the premium segment, as they are today. EV’s will be popular and available across all vehicle variants and prolific in the commercial vehicle industry and in public transportation. Owners and fleet providers will experience the lower costs of electricity, lower maintenance costs, and the lower overall total cost of ownership (TCO). Fully autonomous or self-driving vehicles will introduce design freedom never experienced before, with the removal of the steering wheel, foot pedals and conventional dashboard. Communication and comfort will be re-imagined, with a vehicle that’s no longer designed around the driver but designed to serve the needs and comfort of the occupants, who are now users instead of owners.
With the rise of mobility services such as Uber, Didi, and a host of others, vehicle ownership is fast becoming an option. In a very short time, especially in urban areas such as China’s mega-cities, it is becoming cost-efficient to subscribe to a monthly ride share service for all of your transportation needs.
Bill Russo, CEO, Automobility LTD
Bill Russo, CEO of China-based Automobility, in a December 2018 article, Competing in the Digital Internet of Mobility, notes that the digital connectivity of these vehicles will open up profit opportunities well beyond the vehicle hardware. He says “An expanded understanding of mobility use cases and tailoring of the mobility hardware ‘form factor’ to the particular mobility need will be a way to create a value proposition that is rooted in the unique riding experience. In the user-centric world where users are passengers, the focus shifts from traditional driver-centric design to a user-centric productivity space. Instead of traveling in the cockpit, we will move in business class or economy class, depending on our preferences and budget.” Cities will be re-imagined in new social opportunities associated with autonomy, as these vehicles will serve the under-served, and infrastructures will shift in purpose to move people, as opposed to moving vehicles.
Where does steel fit?
The steel industry plans to be right in the middle of this revolutionary change. Fleet owners who provide ride hailing and ride sharing services need to manage the total cost of ownership, while maximizing the user experience for added revenue. To be profitable, they’ll want durable, lasting structures that are affordable to own, provide the user motion as well as emotional comfort, while being efficient to operate, and environmentally friendly – and steel is the only material that meets all these requirements.
On Camera Now: George Coates, Technical Director, WorldAutoSteel and Phoenix Group from worldautosteel on Vimeo.
As always, steel is needed for the crash safety structures, and now add battery protection. Our market intelligence shows that due to the high cost to municipalities and regional governments, autonomous-only vehicles will be limited to dedicated areas for a long time to come. Meanwhile, vehicle-to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure connectivity will result in dramatic improvements in accident avoidance and reduced fatalities.
Because it will take many years before all vehicles on the road have these technologies in play, the need for passive safety will remain for the foreseeable future. Developing a structural design for the passenger compartment becomes challenging, since there’s a now a need to strike a balance between occupant safety and the occupant freedom. This is enabled by removing the driver and controls from the interior. Steel will be needed to provide the unique properties of both crash energy absorption and deflection, while also managing the loads associated with passengers in multiple and diverse seating configurations. Steel has the ability to provide needed strength while keeping the material thin, which lends more room in the passenger cabin for new seating arrangements and more seats. And battery housings made from steel will provide structural integrity for crash management, while also preventing battery pack damage and leakage.
Lightweighting will continue to be important in an effort to balance smaller battery sizes with maximum range. The steel industry has been and will continue to develop products, such as the ever-growing family of Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS), to meet both the mass reduction and the safety targets, affordably. With content innovation and the amazing flexibility of the Iron (Fe) element, researchers still have vast development possibilities for new steels that are stronger, more formable and cost effective.

Blog
Product benchmarking is the process of measuring and analyzing the performance of competitive products. Data from a benchmarking analysis is used at the early stages of product development where performance targets are being set for a new vehicle. As an example of benchmarking, consider setting the mass target for the body structure of a new vehicle program. We want to set a target that is light weight, but also one that is possible to achieve. We benchmark two competitive body structures to help us set the target, Figure 1.

Figure 1: Mass data for two benchmarked vehicles.
From this limited data, it appears a sufficient target for the new program would be 300 kg, the lighter of the two. But there are questions to be resolved: Are these two structures representative of efficient light weighting? Also, if the vehicle under design is of a slightly different size than these two vehicles, how will this affect the applicability of benchmark comparison?
A means to begin to address these concerns is simply to look at more benchmark vehicles. The tear-down database at A2Mac1 Automotive Benchmarking contains mass data for several hundred vehicles. From this database, structure mass for 280 steel sedans is plotted in Figure 2. This expanded data allows us to see a more complete picture of the range of mass exhibited in the market place. Vehicle A and B considered before no longer stand out as exceptional. While this additional data provides an understanding of the average and range of body structure mass, there are concerns with interpreting this chart. Do the lighter structures represent efficient designs or are they just the structures of smaller vehicles?
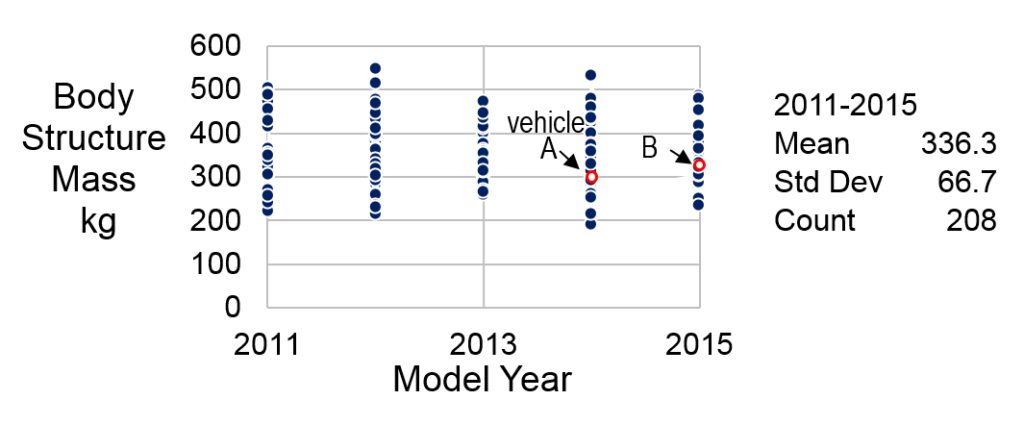
Figure 2: Body structure mass data for 280 benchmarked vehicles.
We can answer this question by investigating how structure mass varies with mass drivers. Two mass drivers for body structure are vehicle size as measured by plan view area, and structural loading taken to depend on the Gross Vehicle Mass. In Figure 3 we use the same vehicles shown in Figure 2, but now plot structure mass versus each mass driver.
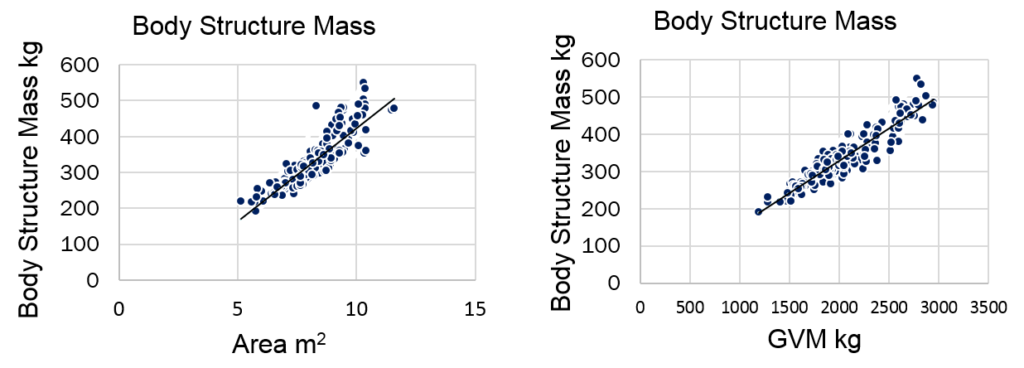
Figure 3: Structure mass vs. vehicle plan view area (left), and gross vehicle mass (right).
The correlation of structure mass for each of these mass drivers is very clearly demonstrated by the trend lines shown: Body structures are heavier for larger cars (left graph), and heavier when they must support greater vehicle mass (right graph). We can quantify these correlations with an equation determined by statistical regression, Equation 1. This equation represents the mass of an average or typical body structure, given its GVM and Area.
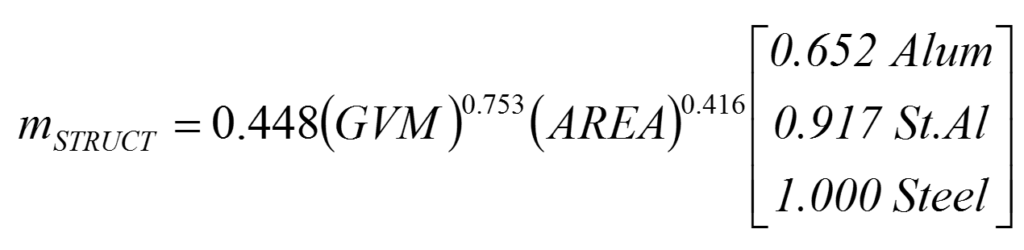
Equation 1
where
mSTRUCT=Mass of body structure (kg)
GVM =Gross vehicle mass (kg)
Area =Plan view area (Length x Width) (m2)
Now for each of the vehicles in our original data set we can calculate the expected structure mass using the vehicle’s GVM and Area. Figure 4 plots the actual measured structure mass vs. the mass expected for that vehicle using Equation 1. The diagonal line indicates those vehicles where the body mass is average or typical. For those structures above the line, body mass is heavier than expected given the area and GVM of the vehicle. And for those below the line, body mass is lighter than expected. This group below the line are the mass efficient body structures that are of interest for fuller analysis.
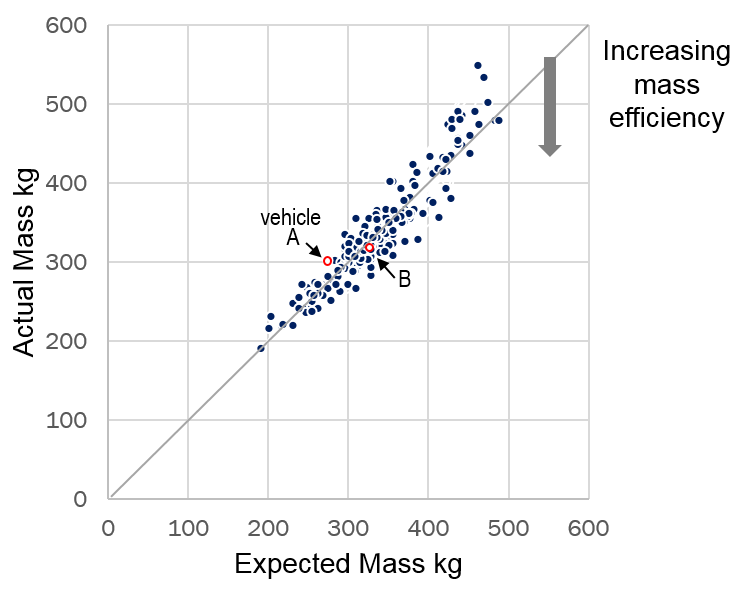
Figure 4: Actual measured structure mass compared to that expected using equation 1.
Note that looking only at structure mass, as in Figure 2, does not lead to understanding which structures are efficient. For example, Vehicle A in Figure 1 is the lighter of the two structures, 300 kg vs. 325 kg. However, after accounting for the two vehicle’s area and GVM, it can be seen from Figure 4 that Vehicle A is above the diagonal line, indicating a heavier than expected structure, while Vehicle B is on the line indicating it has a typical structure mass.
As a further example, consider the WorldAutoSteel FutureSteelVehicle (FSV). The FSV project, completed in 2011, investigated the weight reduction potential enabled with the use of Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS), advanced manufacturing processes, and the use of computer optimization. The resulting material use and body structure mass are shown in Figure 5.
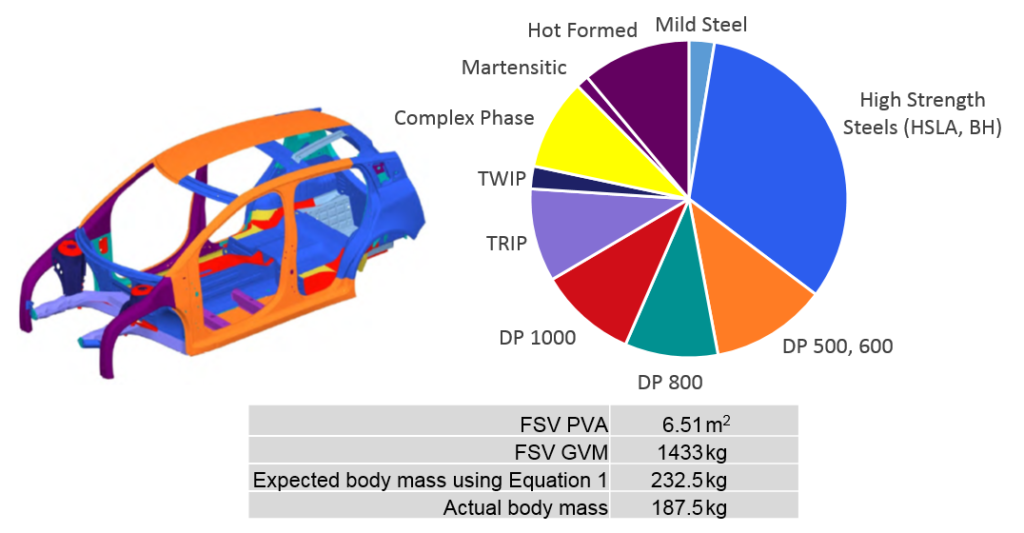
Figure 5: FSV material application and resulting body structure mass.
We can now graph the actual FSV structure mass with expected mass, Figure 6. The data point is well below the diagonal line quantifying the exceptional mass reduction enabled through extensive AHSS use.

Figure 6: FSV body structure compared with 280 normalized benchmarked structures.
Finally, statistical benchmarking reveals which current products would benefit most from lightweighting. Looking again at the plot of actual vs. expected body structure mass for a fixed expected mass, in this case 300 kg, Figure 7. For this set of similarly sized vehicles, there is a wide range of variability in actual mass, indicated by the arrow. For the several vehicles above the diagonal, these body structures are heavier than expected and have significant potential for lightweighting.

Figure 7: Variability in structure mass for similar size vehicles.
For more information on the statistical benchmarking method, see the studies referenced in No. 2 and 3 below. Dr. Malen’s statistical benchmarking methodology also is documented in SAE Paper No. 2015-01-0574
References:
1. A2Mac1.com, Automotive benchmarking.
2. Malen, D., Nagaraj, B., Automotive Mass Benchmarking 2017 study
3. Hughes, J. & Malen, D., Statistical Benchmarking of Automotive Closures, Great Designs in Steel, 2015,
4. FutureSteelVehicle Overview Report, April 2011,

Dr. Donald E. Malen University of Michigan
Dr. Donald E. Malen is an adjunct faculty member at the University of Michigan where he teaches graduate level courses in Automobile Body Structure and Product Design. Prior to this, he was an engineer with General Motors Corporation for 35 years. His background at GM was in automotive body structure design and analysis, and systems engineering. While at GM, he worked on many new vehicle programs and has brought this experience to his teaching and writing. Dr. Malen consults and conducts international seminars on Body Engineering, Innovation, Lead Time Reduction, and Decision Making During Preliminary Design. He holds several patents related to automobile body structure and vibration. His education includes a Ph.D. in Mechanical and Industrial Engineering from the University of Michigan, an MS from Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and a BSME from General Motors Institute (Kettering University).