Ferrite-Bainite (FB) steels are hot rolled steels typically found in applications requiring improved edge stretch capability, balancing strength and formability. The microstructure of FB steels contains the phases ferrite and bainite. High elongation is associated with ferrite, and bainite is associated with good edge stretchability. A fine grain size with a minimized hardness differences between the phases further enhance hole expansion performance. These microstructural characteristics also leads to improved fatigue strength relative to the tensile strength.
FB steels have a fine microstructure of ferrite and bainite. Strengthening comes from by both grain refinement and second phase hardening with bainite. Relatively low hardness differences within a fine microstructure promotes good Stretch Flangable (SF) and high hole expansion (HHE) performance, both measures of local formability. Figure 1 shows a schematic Ferrite-Bainite steel microstructure, with a micrograph of FB 400Y540T shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Micrograph of Ferrite-Bainite steel, HR400Y540T-FB.H-21
The primary advantage of FB steels over HSLA and DP steels is the improved stretchability of sheared edges as measured by the hole expansion test. Compared to HSLA steels with the same level of strength, FB steels also have a higher strain hardening exponent (n-value) and increased total elongation. Figure 3 compares FB 450/600 with HSLA 350/450 steel. Engineering and true stress-strain curves for FB steel grades are shown in Figure 4.
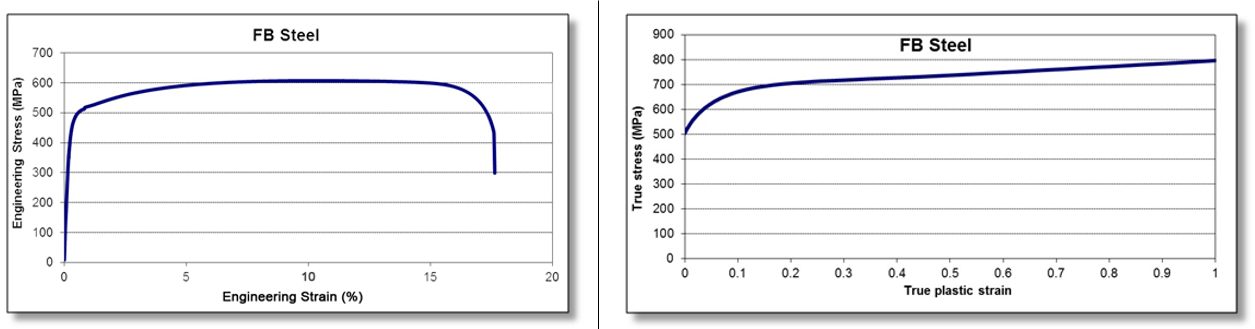
Figure 4: Engineering stress-strain (left graphic) and true stress-strain (right graphic) curve for FB 450/600.T-10
Examples of typical automotive applications benefitting from these high strength highly formable grades include automotive chassis and suspension parts such as upper and lower control arms, longitudinal beams, seat cross members, rear twist beams, engine sub-frames and wheels.
Some of the specifications describing uncoated hot rolled 1st Generation ferrite-bainite (FB) steel are included below, with the grades typically listed in order of increasing minimum tensile strength and ductility. Different specifications may exist which describe uncoated or coated versions of these grades. Many automakers have proprietary specifications which encompass their requirements.
- EN 10338, with the terms HDT450F and HDT580F D-18
- VDA239-100, with the terms HR300Y450T-FB, HR440Y580T-FB, and HR600Y780T-FB V-3
- JFS A2001, with the terms JSC440A and JSC590AJ-23