In production, part geometry or joint application requires the use of gas metal arc welding (GMAW) to weld the joint. A commonly used Advanced High-Strength Steel (AHSS) is Dual Phase (DP) 600 which contains a hard martensite phase in a ferrite matrix (approximately 5-20% martensite). Under the heat input from GMAW, this microstructure near the weld [in the Heat Affected Zone (HAZ)] is destroyed, and a new microstructure develops. Researchers from RWTH Aachen University in GermanyR-24 used representative volume elements (RVE) in tandem with electron probe microanalysis and micromechanical finite element (FE) modeling to develop flow curves for 2.5 mm hot rolled DP 600 steel sheet. This can be used to help predict mechanical properties in the HAZ. The researchers observed bainite, coarse grain ferrite, and tempered martensite in the HAZ.
The researchers developed an engineering stress-strain curve for the GMA welded DP 600 steel as depicted in Figure 1. The stress distribution concentrates to the outside edge of the HAZ as shown in Figure 2, primarily in the softest regions of the HAZ (Figure 3). The soft region is where ductile failure is observed as seen in Figure 4. The soft region is a result of a loss of bainite and an increase in ferrite grain growth. Because ferrite is steel’s softest phase, it results in this soft region where plastic strain accumulates. The increasing presence of tempered martensite starts to raise hardness after this region.
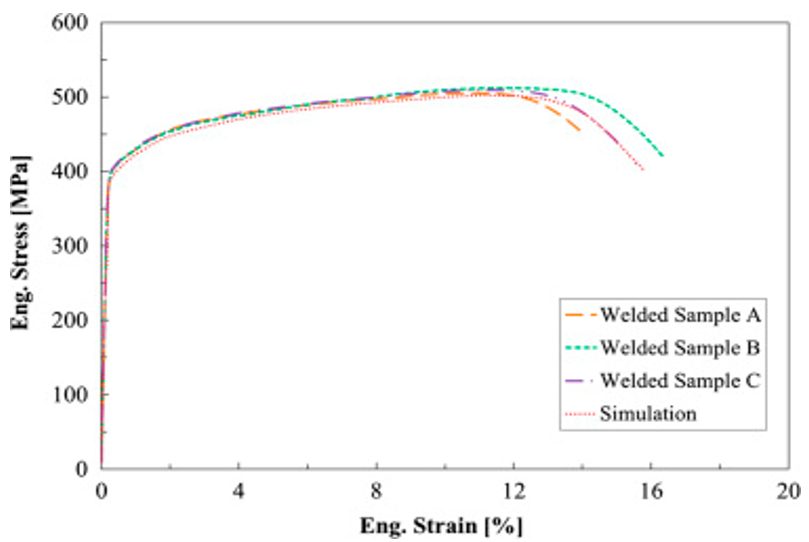
Figure 1: Stress-Strain Curve for GMA Welded DP600 Steel.R-24
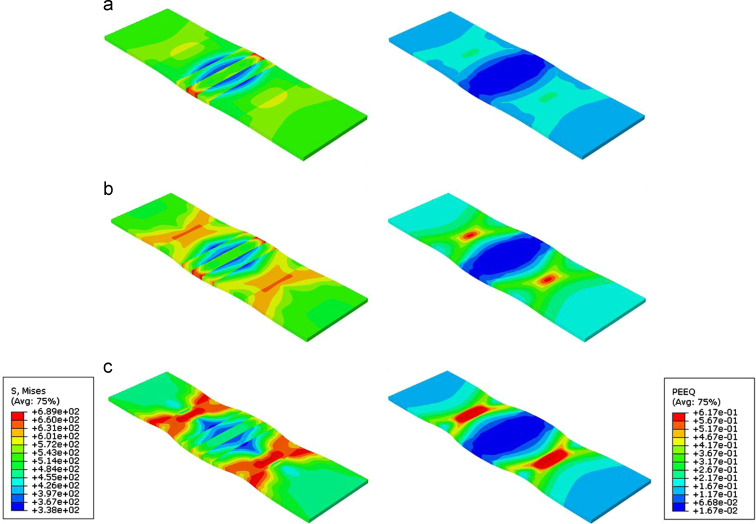
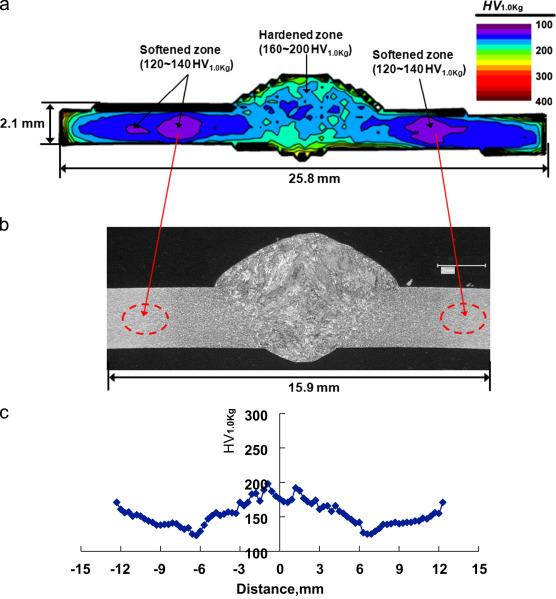
Figure 2: Hardness Map through FZ and HAZ with emphasis on softened zone.R-24
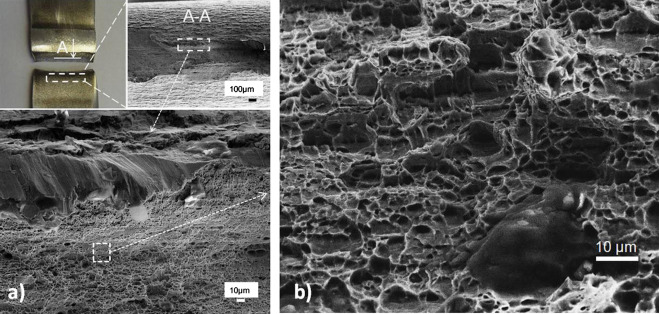
Figure 4: Ductile fracture in softened zone.R-24
The HAZ is composed of a variety of microstructures that vary depending on their distance from the centerline. Close to the middle of the fusion zone, the microstructure is almost 100% bainite with small amounts of ferrite and martensite. Bainite is harder than the tempered steel/ferrite combination, which accounts for the hardness of the fusion zone. Away from the fusion zone, the bainite decreases, and the ferrite increases to where the microstructure is roughly 90% ferrite and 10% martensite, with no bainite in the microstructure (Figure 5).
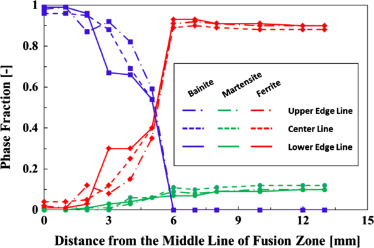
Figure 5: Phase fractions relative to weld centerline.R-24