In order to improve the microstructure and mechanical properties of Aluminium/Steel resistance spot weld joints, Qiu et al.Q-6 tried a new welding method called resistance element welding (REM), i.e, resistance spot welding with a rivet. In this joining method, a hole was drilled in the overlap area of aluminium alloy sheet and a steel rivet was inserted into the hole. Then resistance spot welding was conducted on the rivet. The schematic of the setup was shown in Figure 1. A 4 µm-thick FeAl IMC layer formed at the rivet/Al interface, while FeAl3 formed at the Aluminium/Steel interface. Maximum tensile shear strength of 3.85 kN and pull-out failure mode can be obtained with a welding current of 21 kA, which was much higher than without a rivet (2.8 kN). Crack propagated along the Aluminium/Steel interface until it was arrested by the rivet. Then the crack propagated along the Al/rivet interface until failure.
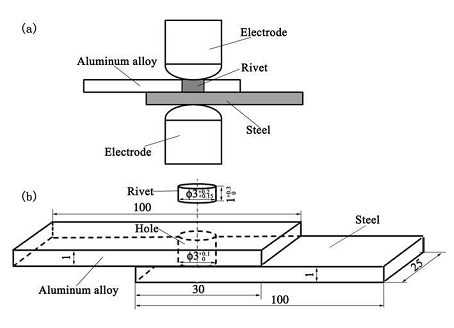
Figure 1: (a) Schematic diagram of resistance spot welding with a rivet; (b) configuration and dimension of the sample (in mm).L-9
Recently, Ling et al.L-9 tried resistance element welding of 2-mm-thick 6061-T6 aluminium alloy with a 1.4-mm-thick galvanized DP780 Dual Phase steel with a 5-mm diameter Q235 steel rivet. With optimum welding conditions, the tensile shear strength of resistance element welded Aluminium/Steel can be 7.368 KN with a fracture energy of 18.9 kN, which were 70% and over 6 times higher than those of RSW joints (Figure 2). The fatigue limit of REM joints was 1.8 kN, which was twice those of RSW joints.
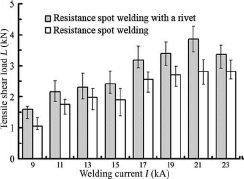
Figure 2: Effect of welding current on the tensile shear load of joints.L-9